Figure 1.
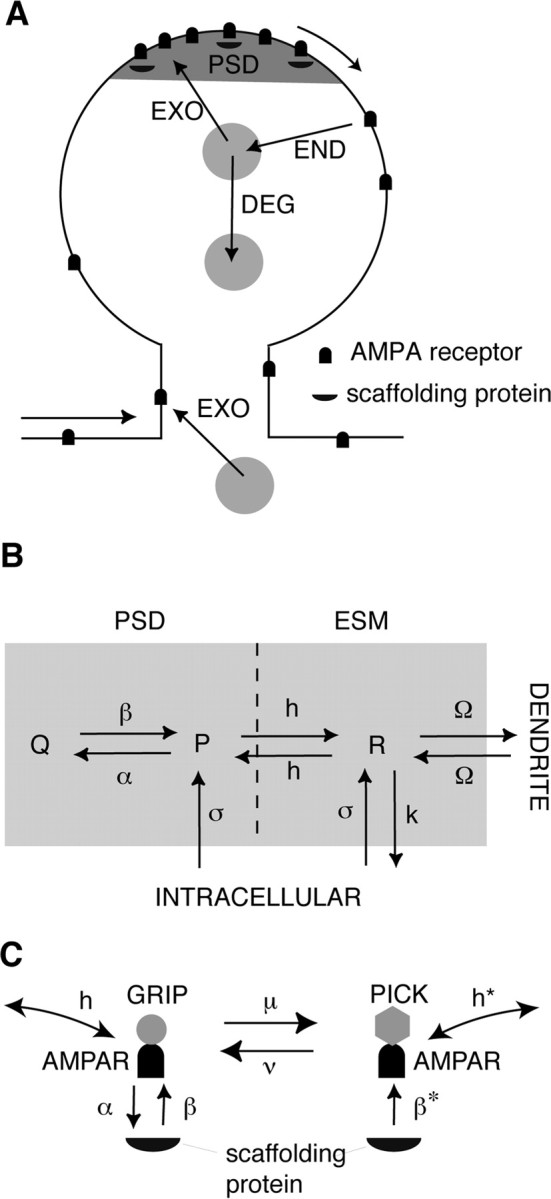
Compartmental model of AMPA receptor trafficking. A, Schematic of AMPA receptor trafficking at a dendritic spine. Receptors stored in intracellular pools are continually exchanged with surface receptors through exocytosis/endocytosis (EXO/END) and sorted for degradation (DEG). Surface receptors diffuse in the dendritic membrane and can be immobilized at the PSD through interactions with scaffolding proteins. B, Simplified two-compartment model of a dendritic spine. Free receptors (concentration P) bind to scaffolding proteins within the PSD to form bound receptors (concentration Q) at a rate α (multiplied by the concentration of free binding sites) and unbind at a rate β. Free receptors flow between the PSD and ESM at a hopping rate h and flow between the ESM and surface of the dendritic cable at a rate Ω. Free receptors (concentration R) within the ESM are internalized at a rate k. Receptors are inserted into the PSD and ESM at a rate σ. Within each compartment, there are two distinct types of receptor corresponding to GluR1/2 (type I) and GluR2/3 (type II) heteromers, respectively. The rates of binding/unbinding, hopping, and exocytosis/endocytosis depend on receptor type. Only type II receptors undergo exocytosis in the PSD (σI = 0) and only type I receptors undergo exocytosis in the ESM (σII = 0). C, LTD model. GluR2/3 receptors are assumed to exist in two distinct states corresponding to association with GRIP and PICK proteins, respectively. Under basal conditions, the transition rate μ from the GRIP-associated state to the PICK-associated state is zero so that only GRIP-associated receptors exist and the model dynamics reduces to the kinetic scheme shown in B. However, during the presentation of an LTD stimulus, μ increases so that some GRIP-associated receptors are converted to PICK-associated receptors. The latter are assumed to rapidly unbind from scaffolding proteins at a rate β*, hop from the PSD to the ESM at a rate h*, where they are endocytosed. This results in a net loss of receptors from the PSD.
