Figure 7.
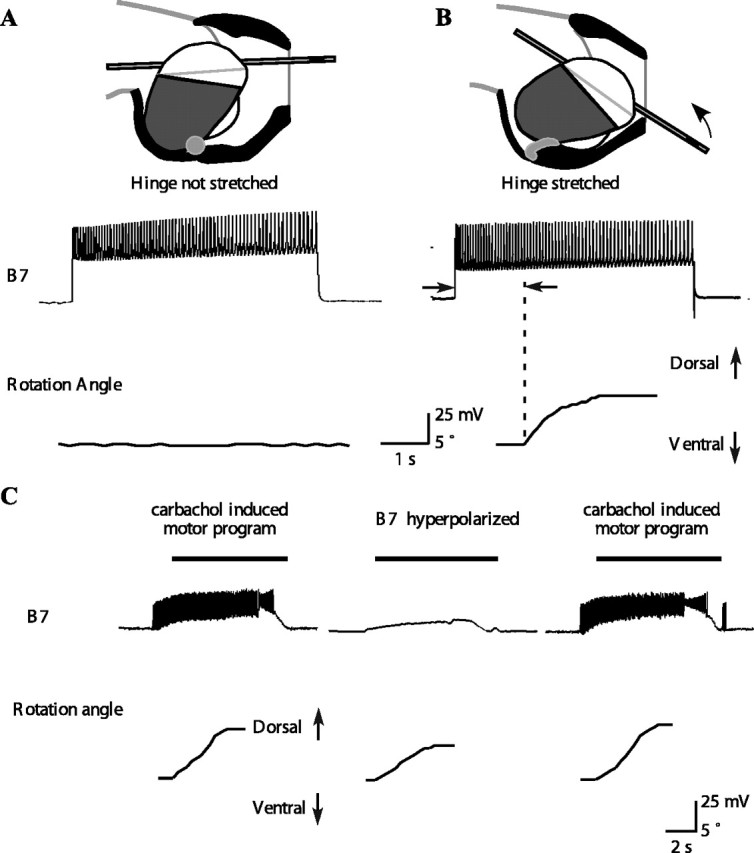
A B7 motor neuron can induce inward tube movement and a dorsal tube rotation if the hinge muscle is stretched either in isolation or during feeding motor programs. A, Top shows a schematic diagram of the peak protraction of a type A swallow. Based on previous in vitro studies (Sutton et al., 2004a), hinge stretch was estimated from the position of the tip of the odontophore. In the experiment shown in the bottom, the hinge was stretched to 0.19 buccal mass lengths. Activating B7 caused no rotation of the tube. In general, B7 had no effect when the hinge was stretched to a length near the minimum hinge stretch estimated from in vivo magnetic resonance images of swallows (Sutton et al., 2004a). The experiment was repeated four times at an average stretch of 0.21 ± 0.03 buccal mass lengths, and activating B7 had no effect in any of these experiments. B, Top shows a schematic diagram of the peak protraction of a type B swallow. The arrow shows the direction of tube inward movement and dorsal rotation. In the experiment shown in the bottom, the hinge muscle was stretched to 0.34 buccal mass lengths. Activating B7 caused a dorsal rotation of the hinge. The minimum stretch of the hinge at which B7 could begin to exert force was 0.35 ± 0.02 buccal mass lengths (n = 4). These values were similar to the maximum hinge stretch during swallowing estimated from in vivo magnetic resonance images (Sutton et al., 2004a). C, During carbachol-induced feeding motor programs, B7 strongly depolarizes and fires action potentials at the same time that the tube moves inward and rotates dorsally. Hyperpolarizing B7 (middle) significantly reduces the inward movement and dorsal rotation. Black bars above the B7 traces indicate the timing of the retraction phase. The magnitudes of the inward movement and rotation are restored when B7 is no longer hyperpolarized (n = 19 from 3 different animals; overall MANOVA highly significant, p < 0.05 for each individual comparison; the inward movement was reduced from 3.9 ± 0.9 to 2.1 ± 0.7 mm).
