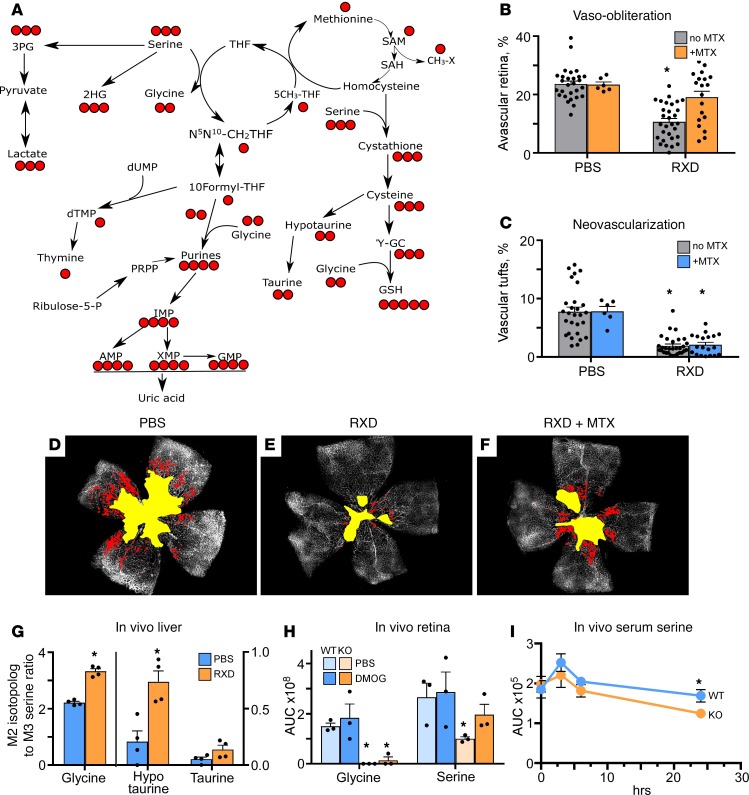
Figure 3. Hepatic 1CM drives protection against OIR.
(A) Schematic showing atom transitions in all aspects of 1CM. (B) Quantification of newborn mice treated with PBS or PBS plus methotrexate (MTX) compared with Roxadustat (RXD) or RXD plus MTX. There was increased vaso-obliteration in the RXD plus MTX group. MTX did not worsen the control group but did worsen the RXD group, showing that hyperoxia downregulates 1CM to such an extent that it is not additive to creating pathology. Under HIF stabilization, 1CM is upregulated and this is blocked by MTX. (C) Quantification of pathological angiogenesis or neovascularization shows that 1CM has no effect on proliferation presumably because it was administered only in phase 1. (D) Representative flat mount from control PBS-injected newborn mouse shows capillary dropout (yellow) and neovascularization (red). (E) Mouse pup retinal flat mount protected by HIF stabilization using RXD. (F) MTX plus RXD (RXD + MTX) demonstrates reduction in protection when 1CM is blocked by dihydrofolate reductase. (G) [13C3] serine injected subcutaneously was followed in liver extracts, demonstrating conversion to M2 glycine, M2 hypotaurine, and M2 taurine, all metabolites of 1CM. (H) The change in retinal serine and glycine using a hepatic-specific HIF stabilizer in wild-type (WT) versus HIF-1α2lox/2lox albumin-Cre–knockout (HIF-1α–KO) mice. (n = 6 animals in each group.) (I) Serum serine and glycine levels in the WT versus HIF-1α2lox/2lox, DMOG-injected mouse metabolite extracts. Metabolites were extracted from the serum at different time points after DMOG i.p. injections. *, 2-tailed t test P values less than 0.05.