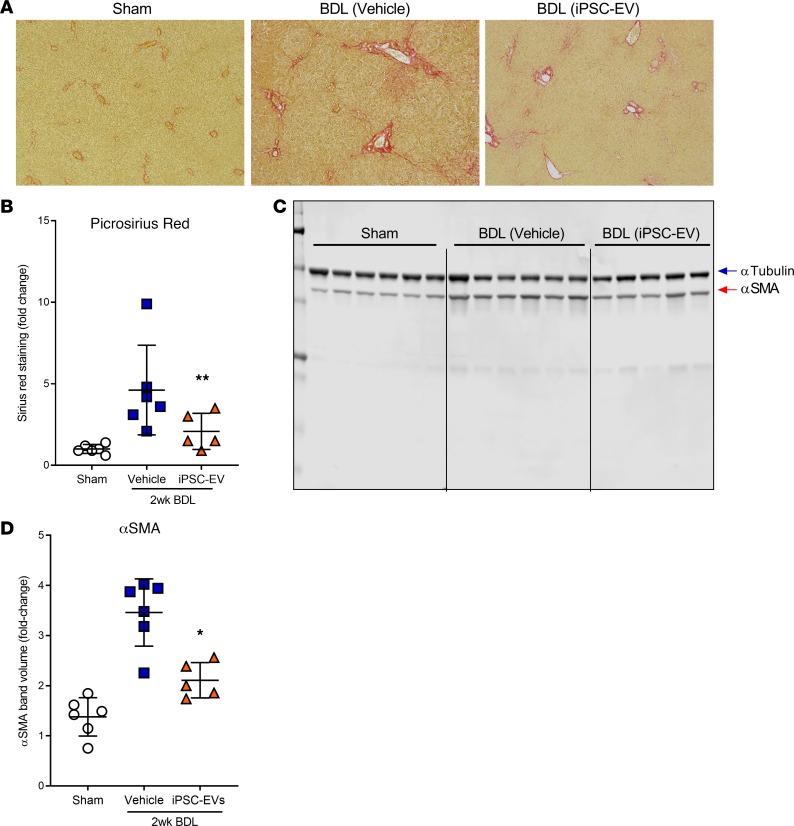
Figure 5. Intravenous administration of m–iPSC-EVs reduces development of fibrosis and HSC activation in an experimental model of cholestatic liver fibrosis.
(A) Representative microphotographs and (B) corresponding quantification graph of Picrosirius red staining of liver sections harvested from mice that received common bile duct ligation (BDL) for 2 weeks (n = 5–6 mice/group) and were administered, by tail vein, mouse iPSC-EVs (BDL iPSC-EVs) or vehicle control (BDL vehicle) for the last 6 days of the study. Mice that underwent abdomen laparotomy but did not receive BDL were used as no-disease controls (sham). Original magnification, ×10. (C) Immunoblots and (D) corresponding quantification graph of αSMA protein levels over 2 weeks in BDL mice treated with mouse iPSC-EVs or with vehicle for the last 6 days of the study. Tubulin was used as a loading control for Western blots. Values represent mean ± SD. *P < 0.05, and **P < 0.005; Kruskal-Wallis test with post hoc Mann-Whitney test and Bonferroni’s correction were used for statistical analysis.