Figure 3.
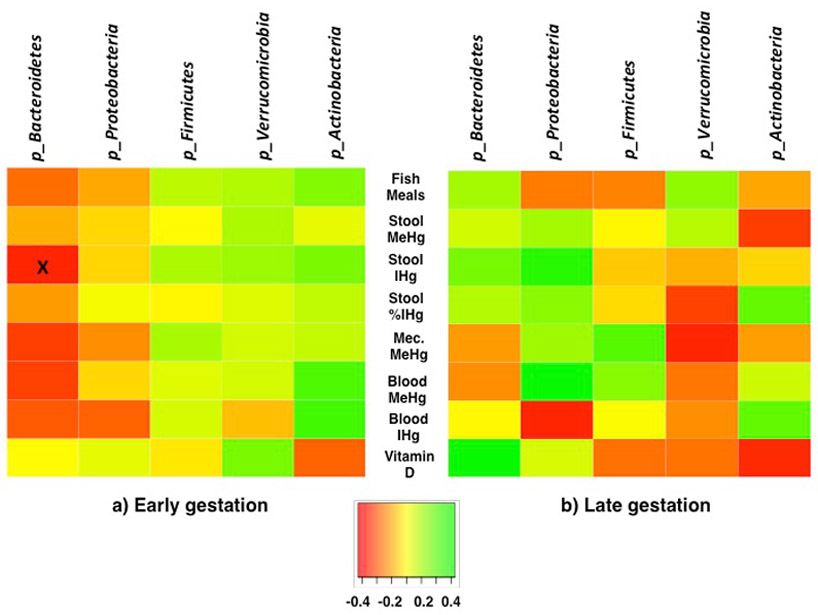
Spearman's correlation between gut microbiota phyla, and fish meals (meals/weekly), stool methylmercury (MeHg) (ng/g), stool inorganic mercury (IHg) (ng/g), stool IHg (% of THg), meconium (Mec) MeHg, blood MeHg (μg/L), blood IHg (μg/L), and plasma vitamin D (25-hydroxy-vitamin D) (ng/mL), during a) early gestation and b) late gestation. During early gestation n=28, except vitamin D (n=22), and meconium MeHg (n=17). During late gestation n=24, except vitamin D (n=21), and meconium (n=17). Note that fish meals and meconium did not differ between early and late gestation, whereas biomarkers for stool and blood MeHg and IHg, and plasma vitamin D were analyzed at each time point. "x" p<0.05.
