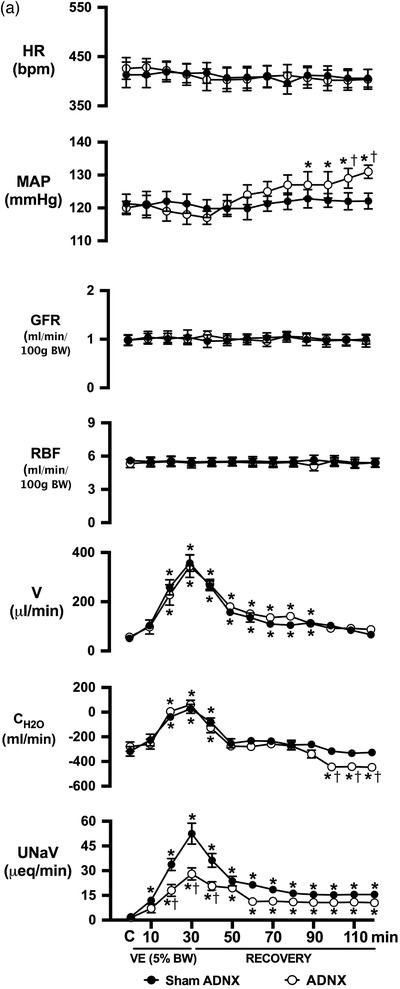
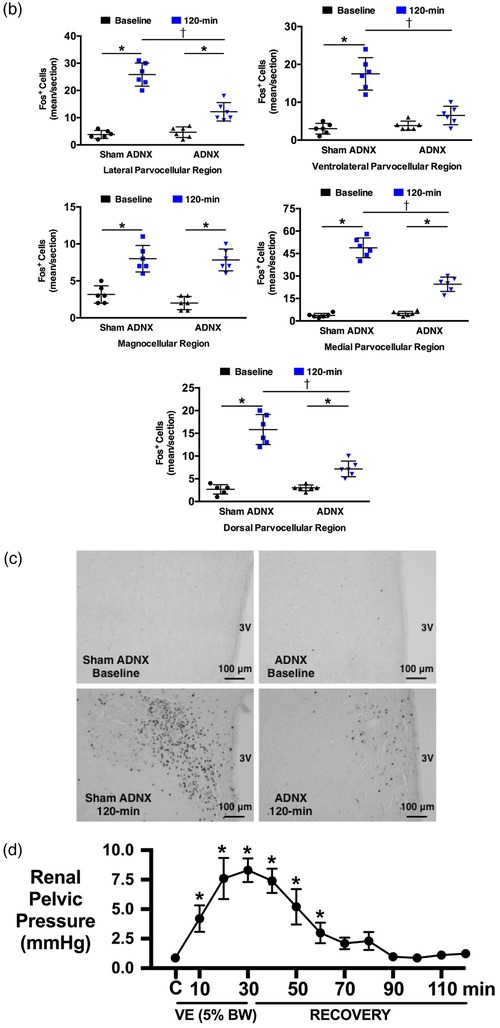
Figure 1.
Effect of selective afferent renal nerve ablation on the cardiovascular, renal and PVN neuronal responses to an acute volume expansion. (a) Cardiovascular and renal responses to a 30 min 5% body weight isotonic saline volume expansion (VE) followed by a 90 min recovery period in conscious male Sprague–Dawley (SD) rats 10 days after a selective afferent renal nerve ablation (ADNX) or sham ADNX procedure. (b) Neuronal activation (c‐fos‐positive cell count) in the lateral parvocellular, ventrolateral parvocellular, magnocellular, medial parvocellular and dorsal parvocellular regions of the paraventricular nucleus (PVN) of the hypothalamus following VE or a 2 h surgical recovery and control period (baseline group) in conscious male SD rats 10 days after a sham or ADNX procedure. (c) Representative images from level 2 of the PVN. (d) Renal pelvic pressure in a separate group of anaesthetized male SD rats during a control period (denoted C), a 30 min 5% isotonic saline VE period and a 90 min recovery period. n = 6/group. *P < 0.05 vs. group baseline value, denoted C; †P < 0.05 vs. respective sham ADNX value. CH2O, free water clearance; GFR, glomerular filtration rate; HR, heart rate; MAP, mean arterial pressure; RPF, renal plasma flow; U Na V, urinary sodium excretion; V, urinary flow rate