Figure 1.
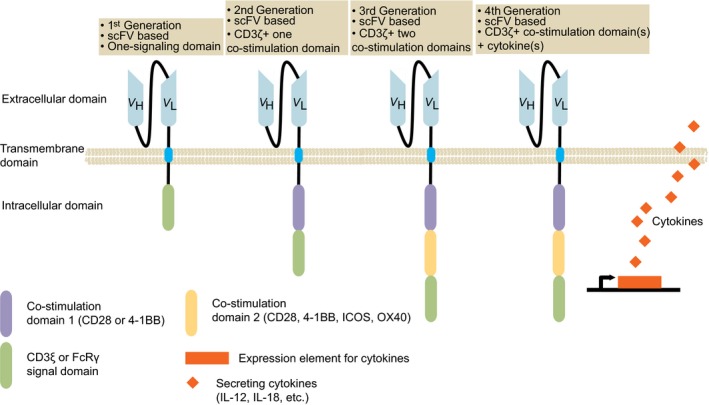
Different generations of CAR. The basic design of CAR is composed of an extracellular binding domain (usually a scFv), a hinge, transmembrane domain and one to three intracellular domains. The fourth‐generation‐CAR‐T cells are engineered to deliver a transgenic payload, such as proinflammatory cytokines, released upon engagement of CAR with its target. CAR, chimeric antigen receptor; scFv, single‐chain variable fragment
