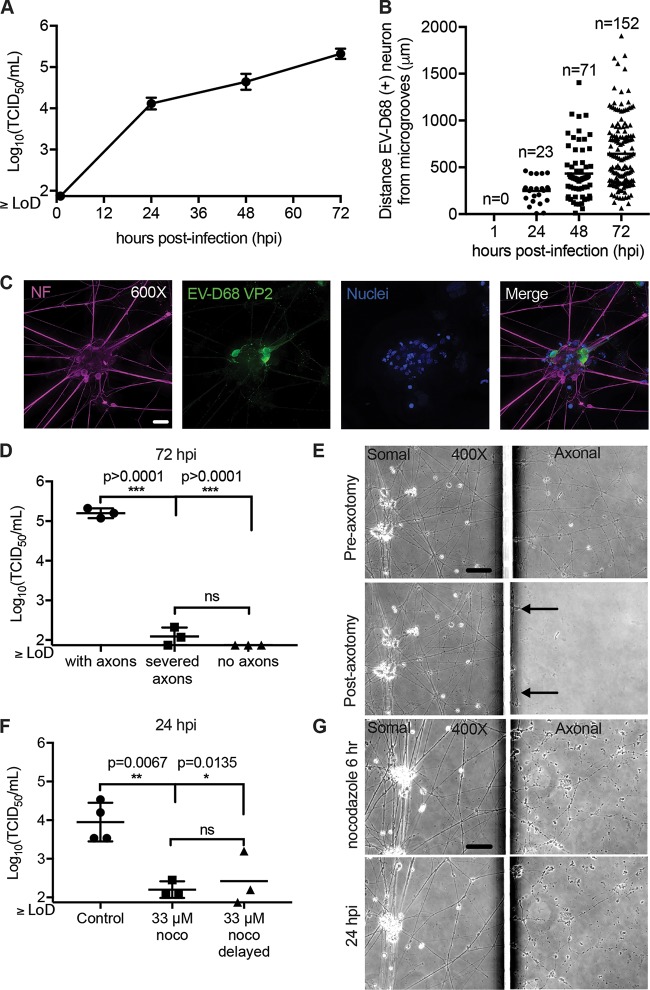
FIG 3.
Retrograde axonal transport of EV-D68 in human iPSC motor neurons. (A) iPSC motor neuron axons on the axonal side of the microfluidic chambers were infected with 1 × 105 TCID50 of EV-D68 IL/14-18952 for 1 h and then thoroughly rinsed. Chambers (n = 3 per time point) were collected a 1, 24, 48, and 72 h postinfection (hpi) and evaluated for viral growth by TCID50 assay. (B) Additional chambers (n = 1 per time point) were infected on the axonal side as described in the legend to panel A and evaluated for the number of infected neurons and their distance from the microgrooves at 1, 24, 48, and 72 hpi by immunohistochemistry (IHC). No infected neurons were detected at 1 hpi. The number of EV-D68-infected neurons per chamber increased from 24 hpi to 48 hpi and from 48 hpi to 72 hpi, with infected neurons appearing further from the microgrooves over time. (C) Example images of iPSC motor neurons at 48 hpi showing EV-D68 VP2 antigen within their cell bodies and dendrites following axonal infection. (D) Chambers with iPSC motor neuron axons intact (n = 3), axons severed by axotomy (n = 3), and chambers in which motor neurons were grown in such a way to prevent axons from crossing the microgrooves (n = 3) were infected on the axonal side described for panel A and then evaluated for viral growth at 72 hpi. A significant reduction in viral growth was seen in severed axons and under no-axon conditions compared to that for the control with axons, as evaluated by one-way ANOVA followed by Tukey’s multiple-comparison test. hiPSC, human iPSC. (E) Phase-contrast images of iPSC motor neurons from chambers pre- and postaxotomy (right images) demonstrate that axotomy did not affect the somal side of the chamber (left images). Black arrows indicate that a few small strands of axon did remain close to the microgrooves after axotomy. (F) Chambers with iPSC motor neurons were treated with the reversible microtubule toxin nocodazole (noco) (n = 3) or the DMSO control (n = 4) on the axonal side for 1 h prior to infection, during axonal infection, and for 4 h after infection (6 h total). For one group, nocodazole treatment was delayed until 30 min after the start of viral infection (n = 3). A significant reduction in viral titer was seen in the somal side at 24 hpi, as evaluated by one-way ANOVA followed by Tukey’s multiple-comparison test. (G) Phase-contrast images of iPSC motor neuron chambers at the end of the 6-h nocodazole treatment and at 24 hpi demonstrate that axons remained in the axonal side (right images) after treatment but showed some thinning and varicosities. Nocodazole did not affect the somal side of the chambers (left images). Bars = 50 μm for the ×400-magnification images and 20 μm for the ×600-magnification images. LoD, limit of detection.