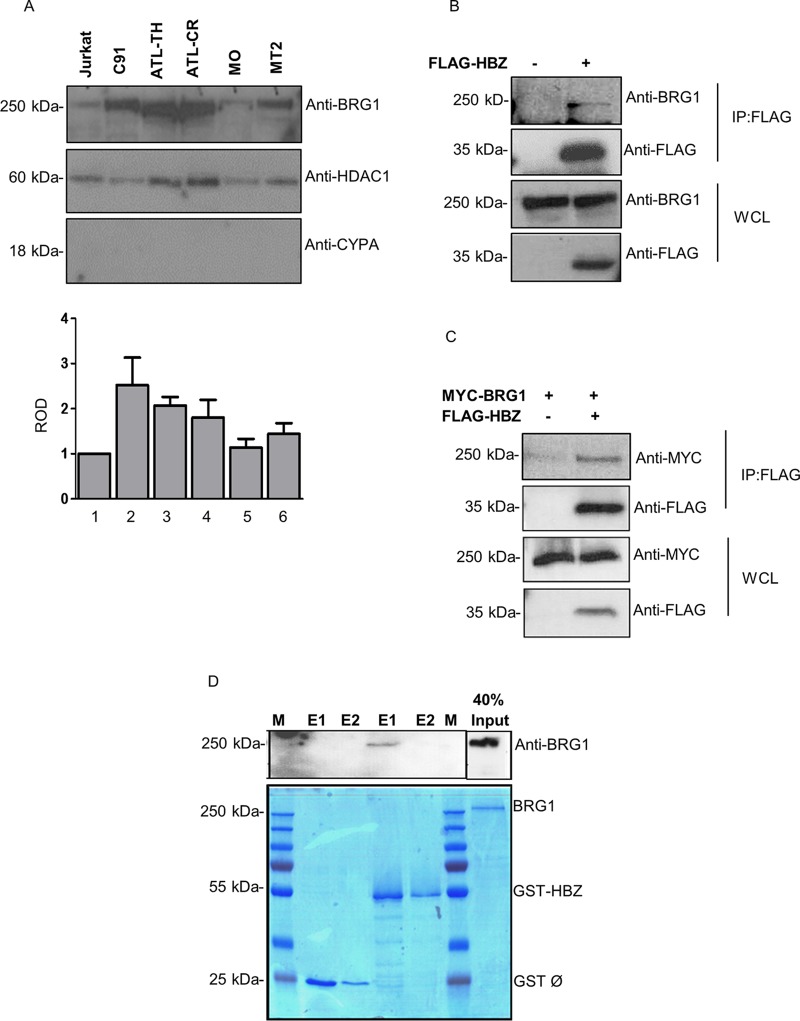
FIG 1.
HTLV-1 HBZ antisense protein interacts with BRG1. (A) BRG1 expression levels in HTLV-1/2-infected T cells and uninfected cells. Nuclear fractions from HTLV-1-positive cell lines (C91 and MT2), an HTLV-2-positive cell line (MO), ATL patient cell lines (ATL-CR and ATL-TH), and HTLV-1-negative T-cell lymphoma cells (Jurkat) were isolated using a nuclear and cytoplasmic extraction kit from Pierce (NE-PER). The expression of BRG1 was detected using anti-BRG1. Anti-HDAC1 was used as a loading control. Anti-CYPA was used as an indicator of the integrity of the nuclear fractions. The bottom panel represents the relative optical density (ROD) of BRG1 expression normalized against HDAC1. (B and C) HBZ interacts with endogenous (B) and exogenous (C) BRG1 in mammalian cells. HEK293T cells were transfected with 5 μg of FLAG-HBZ or an empty vector alone (B) or together with 6 μg of a MYC-tagged expression vector for BRG1 (C). Transfected cells were lysed after 24 h, and coimmunoprecipitations were performed using anti-FLAG M2 beads overnight. Interactions were analyzed by Western blotting using anti-FLAG, anti-BRG1, and anti-MYC antibodies, as indicated. IP, immunoprecipitation; WCL, whole-cell lysate. (D) Direct interaction between HBZ and BRG1 in vitro. GST pulldown assays were performed by incubating purified BRG1 protein (6 μg) with GST resins precoated with either GST-HBZ or GST proteins. Bound proteins were eluted twice (E1 and E2), and interactions were analyzed by immunoblotting using anti-BRG1 (top) and Coomassie blue staining (bottom). The BRG1 input corresponds to 40% of the total BRG1 loaded for each pulldown. M indicates the protein molecular weight marker.