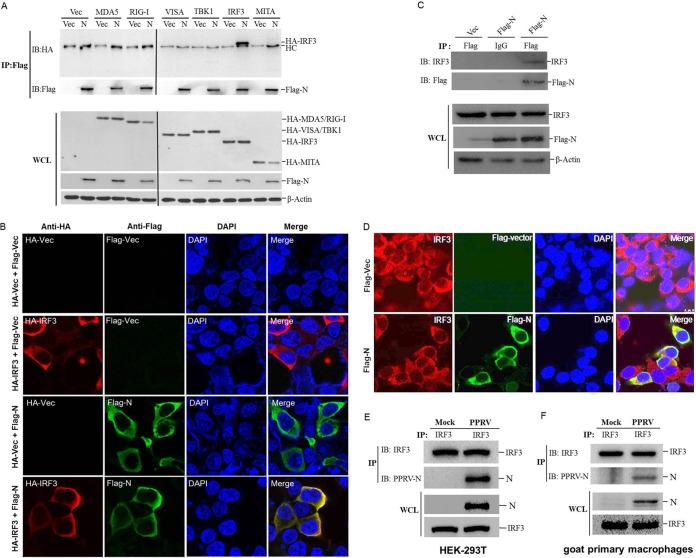
FIG 3.
PPRV N protein interacts with both exogenous and endogenous IRF3. (A) HEK-293T cells were cotransfected with empty vector- or Flag-N-expressing plasmids and the indicated plasmids expressing different HA-tagged adaptor molecules for 48 h. The cells were then lysed and immunoprecipitated with an anti-Flag antibody. The whole-cell lysates (WCL) and immunoprecipitation (IP) complexes were analyzed by Western blotting using an anti-HA, anti-Flag, or anti-β-actin antibody. HC, heavy chain. (B) HEK-293T cells were cotransfected with HA empty vector plasmids or an HA-IRF3-expressing plasmid and Flag empty vector- or Flag-N-expressing plasmids for 36 h. The subcellular localization of HA-tagged IRF3 and Flag-tagged N protein was analyzed by IFA. (C) HEK-293T cells were transfected with empty vector- or Flag-N-expressing plasmids for 48 h. The cells were lysed and immunoprecipitated with an anti-Flag antibody or mouse normal IgG antibody. The WCL and IP complexes were analyzed by Western blotting using anti-IRF3, anti-Flag, or anti-β-actin antibodies. (D) HEK-293T cells were transfected with empty vector- or Flag-N-expressing plasmids for 36 h. The colocalization of endogenous IRF3 and Flag-tagged N protein was analyzed by IFA. (E and F) HEK-293T or goat primary macrophages cells were mock infected or infected with PPRV for 48 h. The cells were lysed and immunoprecipitated with an anti-IRF3 antibody. The WCL and IP complexes were analyzed by Western blotting using anti-IRF3 and anti-N antibodies.