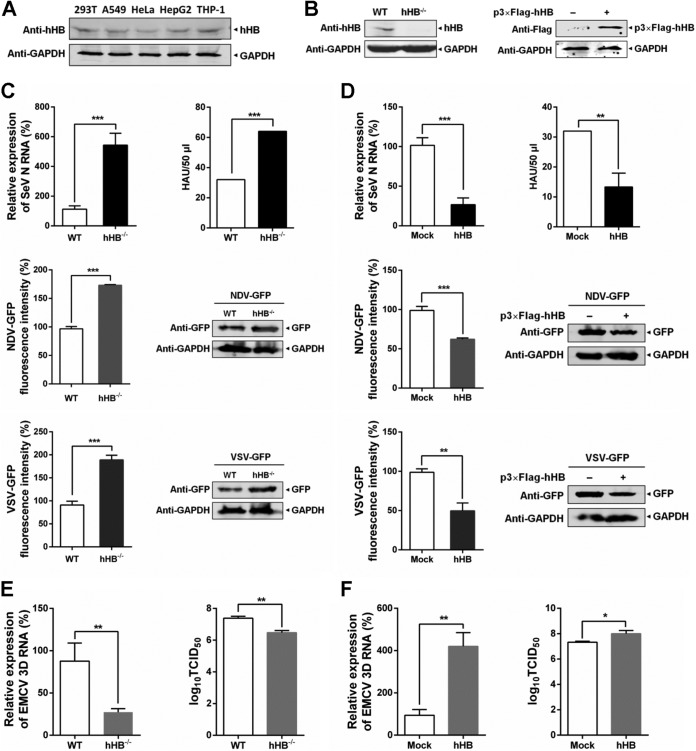
FIG 1.
hHB is involved in the antiviral responses to RNA viruses. (A) The expression of hHB in different nonerythroid cell lines including HEK293T, HepG2, A549, HeLa, and THP-1. (B) The knockout efficiency of hHB in hHB-deficient HEK293T (hHB−/−) cells compared with the expression level of hHB in the wild-type HEK293T (WT). (C) hHB−/− cells were more sensitive to Sendai virus (SeV), vesicular stomatitis virus (VSV), and Newcastle disease virus (NDV) infections. hHB−/− and WT cells were infected with SeV for 24 h or with VSV-GFP or NDV-GFP for 48 h. Then the viral titers of SeV in the supernatants were determined by hemagglutination assay, and the RNA level of the SeV N protein in the cells was determined by real-time RT-PCR. In addition, the GFP expression and fluorescence levels in VSV-GFP- or NDV-GFP-infected cells were analyzed by Western blotting and an Enspire Multimode Plate Reader. HAU, hemagglutinating units. (D) Overexpression of hHB inhibited the replication of SeV, VSV, and NDV. HEK293T cells were transfected with the p3×Flag-CMV-10 empty vector (p3×Flag-EV) or p3×Flag-hHB for 24 h and then infected with SeV for 24 h or with VSV-GFP or NDV-GFP for 48 h. The viral titers of SeV in the supernatants and the RNA level of the SeV N protein in the cells or GFP expression and fluorescence of VSV-GFP or NDV-GFP were tested. (E) The effect of hHB on the replication of encephalomyocarditis virus (EMCV). hHB−/− and WT cells were infected with EMCV for 24 h. Then viral titers (as 50% tissue culture infective dose [TCID50]) in the supernatants and the RNA level of the EMCV 3D protein in the cells were determined. (F) The effect of hHB overexpression on the replication of EMCV. HEK293T cells were infected with EMCV for 24 h. Then the titers in the supernatants and the RNA level of EMCV 3D protein in the cells were determined. The data represent the means ± standard deviations from three independent experiments. Significant differences are denoted as follows: *, P < 0.05; **, P < 0.01; ***, P < 0.001.