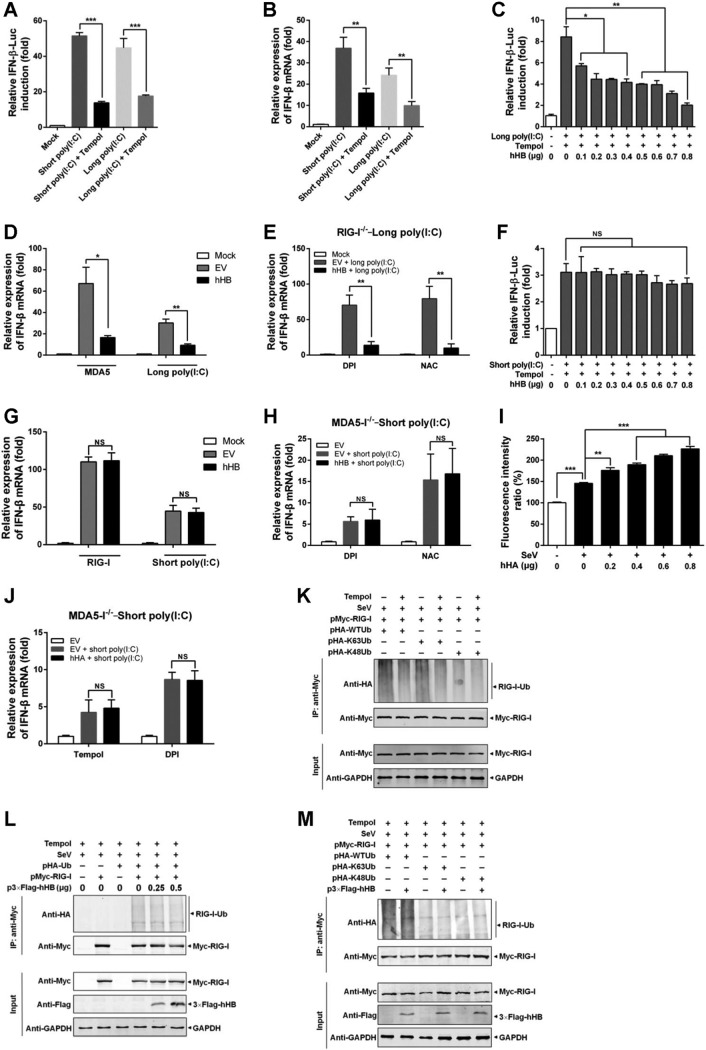
FIG 8.
Tempol inhibits hHB-induced facilitation of the RIG-I signaling pathway but has no effect on hHB-induced inhibition of the MDA5 signaling pathway. (A) The effects of tempol on long-poly(I·C)- or short-poly(I·C)-induced activation of the IFN-β promoter. HEK293T cells were transfected with pRLuc-TK, pIFN-β-FLuc, and long poly(I·C) or short poly(I·C) for 12 h and then treated with 3 mM tempol or PBS for 12 h. The activation of IFN-β promoter was tested. (B) The effects of tempol on long-poly(I·C)- or short-poly(I·C)-induced IFN-β mRNA transcription. HEK293T cells were transfected with long poly(I·C) or short poly(I·C) for 12 h and then treated with 3 mM tempol or PBS for 12 h. The IFN-β mRNA level in cells was analyzed. (C) Tempol suppressed hHB-induced inhibition of the activation of the IFN-β promoter in response to long poly(I·C). HEK293T cells were transfected with the 3×Flag-hHB (hHB) at the indicated concentrations, pRLuc-TK, pIFN-β-FLuc, and long poly(I·C) for 12 h. Then the cells were treated with 3 mM tempol or PBS for 24 h. (D) The effect of tempol on hHB regulation of MDA5-mediated transcription of IFN-β. HEK293T cells were transfected with the p3×Flag-EV or p3×Flag-hHB and pMyc-MDA5 or long poly(I·C) for 12 h. Then the cells were treated with 3 mM tempol or PBS for 12 h. (E) The effect of diphenyleneiodonium chloride (DPI) and N-acetyl-l-cysteine (NAC) on the hHB regulation of MDA5-mediated mRNA transcription of IFN-β. RIG-I−/− cells were transfected with the p3×Flag-EV or p3×Flag-hHB and/or long poly(I·C) for 12 h. Then the cells were treated with 3 μM DPI, 10 mM NAC, or PBS for 12 h. (F) Tempol suppressed hHB-induced upregulation of the activation of the IFN-β promoter in response to short poly(I·C). HEK293T cells were transfected with p3×Flag-hHB (hHB) at the indicated concentrations, pRLuc-TK, pIFN-β-FLuc, and short poly(I·C) for 12 h. Then cells were treated with 3 mM tempol or PBS for 24 h. (G) The effect of tempol on the regulation of RIG-I-mediated IFN-β transcription by hHB. HEK293T cells were transfected with the p3×Flag-EV or p3×Flag-hHB and pMyc-RIG-I or short poly(I·C) for 12 h. Then the cells were treated with 3 mM tempol or PBS for 12 h. (H) The effect of DPI and NAC on the hHB regulation of RIG-I-mediated mRNA transcription of IFN-β. MDA5−/− cells were transfected with the p3×Flag-EV or p3×Flag-hHB and short poly(I·C) for 12 h. Then the cells were treated with 3 μM DPI, 10 mM NAC, or PBS for 12 h. (I) The effect of hHA on the ROS accumulation in SeV-infected cells. HEK293T cells were transfected with p3×Flag-hHA at the indicated concentrations for 24 h and then were infected with SeV. Then the cytoplasmic ROS formation was measured at 12 h after infection. (J) The effect of tempol or DPI on the hHA-mediated regulation of short poly(I·C)-induced IFN-β transcription. MDA5−/− cells were transfected with the p3×Flag-EV or p3×Flag-hHB and short poly(I·C) for 12 h. Then the cells were treated with 3 mM tempol, 3 μM DPI, or PBS for 12 h. (K) The effect of tempol on RIG-I ubiquitination. HEK293T cells were cotransfected with the indicated plasmids. At 12 h after transfection, the cells were treated with 3 mM tempol for 12 h. (L and M) The effect of tempol on hHB-induced RIG-I ubiquitination. HEK293T cells were cotransfected with the indicated plasmids. At 12 h after transfection, the cells were infected with SeV and treated with 3 mM tempol for 12 h. The data represent the means ± standard deviations from three independent experiments. Significant differences are denoted as follows: *, P < 0.05; **, P < 0.01; ***, P < 0.001; NS, not significant (P > 0.05).