Abstract
Cadmium (Cd) is an established carcinogen that is involved in the progression of lung cancer. However, the mechanisms underlying this Cd-induced process have yet to be fully elucidated. The present study explored the potential roles of phosphorylated (p)-ERK in the Cd-induced migration and invasion of lung cancer cells. An MTT assay was performed to evaluate cell viability whilst western blot analysis and reverse transcription-quantitative PCR were used to detect the expression of protein and mRNA, respectively. Migration and invasion assays were performed to assess cell migratory and invasive abilities. The results demonstrated that exposure to Cd increased the expression of p-ERK in A549 cells. Cd also enhanced the migration and invasion of A549 cells, which could be blocked via U0126 treatment (an inhibitor of mitogen activated protein kinase). In addition, it was identified that Cd-induced expression of matrix metalloproteinases 2 mRNA was mediated by p-ERK. In conclusion, the present findings indicated that Cd induced A549 cell migration and invasion by activating ERK, and it was hypothesized that p-ERK could serve as a target in the clinical treatment of Cd-induced lung cancer.
Keywords: cadmium, lung cancer, migration, invasion, phosphorylated-ERK
Introduction
Lung cancer is one of the most common malignant tumors that is a major cause of various cancer-related deaths for men and women, worldwide. In 2012, there were ~1.8 million newly registered cases of lung cancer, with 1.6 million deaths occurring globally (1). Non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) accounts for ~85% of all lung-cancer-related deaths and can be classified as adenocarcinoma (40%), squamous cell carcinoma (<40%) and large cell carcinoma (5%). It is well established that tobacco smoke is the main cause of lung cancer; however, a series of studies have identified that occupational and environmental exposure to cadmium (Cd) is another important risk factor (2–5).
Cd is a widely used toxic industrial heavy metal that causes serious environmental health hazards to humans. The International Agency for Research on Cancer has classified Cd as a known human carcinogen (6). The primary means of Cd intake by humans are via food (particularly plant products), habitual tobacco smoking, drinking contaminated sources and Cd-related industry. Increasing evidence has revealed a correlation between Cd exposure and the formation of lung cancer (2,7,8). It has also been reported that oxidative stress, apoptotic resistance, induction of autophagy, decreased DNA repair capacity and genomic instability are involved in the development of lung cancer induced by Cd (9). Recently, exposure to Cd has been correlated with the migration and invasion of lung cancer cells (10,11). However, the underlying mechanisms of Cd-induced cancer are yet to be fully elucidated.
ERK, a member of the mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) family, is a key molecule that transmits signals from surface receptors to the nucleus. It has the capacity to regulate cell growth, survival, mitosis and differentiation. It has also been demonstrated that ERK is involved in cell migration and invasion in several types of cancers (12–16), including lung cancer (17–24). Quintero Barceinas et al (17) reported that all-trans retinoic acid promoted growth, survival and migration in A549 lung cancer cells by activating the ERK signaling pathway. Furthermore, Li et al (18) reported that angelicin inhibited human lung carcinoma A549 cell growth and migration by regulating the ERK pathway. Zhang et al (20) demonstrated that transmembrane protein 17 decreased the invasion and metastasis of lung cancer cells via the ERK signaling pathway.
Based on previous literature, the present study hypothesized that p-ERK may serve an important role in the migration and invasion of A549 cells induced by Cd. Therefore, the aim of the current study was to explore the potential roles of p-ERK in Cd-induced A549 cell migration and invasion to increase understanding of the underlying molecular mechanisms and provide a potential therapeutic target for lung cancer treatment.
Materials and methods
Cell culture and treatment
The human lung cancer A549 cell line was obtained from the American Type Culture Collection (25). A549 cells were cultured in RPMI-1640 medium (Beijing Solarbio Science & Technology Co., Ltd.) containing 10% fetal bovine serum (FBS) (GE Healthcare Bio-Sciences), 100 U/ml penicillin and 100 µg/ml streptomycin in a humidified incubator at 5% CO2 and 37°C. A549 cells were cultured in serum-free RPMI-1640 medium for 24 h, followed by treatment with different concentrations of Cd [cadmium chloride hemi (pentahydrate); Shanghai Aladdin Bio-Chem Technology Co., Ltd.; 0, 0.1, 0.25, 0.5, 1, 2, 4 or 8 µM] for various durations (0, 8, 24 or 48 h), as indicated. For certain experiments, 10 µM U0126 (Sigma-Aldrich; Merck KGaA), an inhibitor of mitogen activated protein kinase (MEK)1/2 that is widely used to inhibit ERK1/2 activation (26–29), was added to the cell culture 1 h before Cd treatment.
MTT assay
A549 cells were harvested and seeded into 96-well plates at a density of 1×104 cells per well. Following incubation at 37°C for 24 h, the cells were treated with 0, 0.1, 0.25, 0.5, 1, 2, 4 or 8 µM Cd for 48 h at 37°C. MTT (10 µl; 5 mg/ml) was then added to each well and cells were incubated at 37°C for 4 h. Purple formazan was dissolved in 150 µl of dimethyl sulfoxide, and absorbance was measured on a microplate reader at 492 nm. The group treated with 0 µM Cd was regarded as the control. Four replicate wells were used for each analysis.
Western blot analysis
Cells were collected and washed three times with cold PBS. RIPA assay (Pierce; Thermo Fisher Scientific, Inc.) solution containing protease and phosphatase inhibitors was subsequently used to lyse cells, after which the protein content was determined using a bicinchoninic acid assay. Proteins (30 µg) were separated via SDS-PAGE on a 12% gel then transferred onto a nitrocellulose membrane. The membrane was then blocked with 5% bovine serum albumin in Tris-buffered saline and 0.1% Tween-20 (TBST) at room temperature for 1 h. Subsequently, the blots were incubated at 4°C overnight with primary antibodies against phosphorylated (p)-ERK1/2 (1:1,000; Thr202/Tyr204; cat. no. 4730S; Cell Signaling Technology, Inc.), ERK1/2 (1:1,000; cat. no. 4695S; Cell Signaling Technology, Inc.) and tubulin (1:1,000; cat. no. sc-365791; Santa Cruz Biotechnology, Inc.). The blots were then washed with TBST three times, followed by incubation with horseradish peroxidase-conjugated secondary antibodies (Goat anti-rabbit IgG; cat. no. ZB-2301; Goat anti-Mouse IgG; cat. no. ZB-2305; each, OriGene Technologies, Inc.; each, 1:5,000) for 1 h at room temperature. Finally, the protein bands were visualized using an enhanced chemiluminescence reagent (cat. no. #1705060; Bio-Rad Laboratories, Inc.) on a ChemiDoc™ XRS+ image analysis system (Bio-Rad Laboratories, Inc.). Densitometry was performed using Image J software v1.31 (National Institutes of Health).
RNA extraction and reverse transcription-quantitative PCR (RT-qPCR)
Total RNA was extracted from A549 cells using RNAiso Plus (Takara Bio, Inc.) according to the manufacturer's protocol. Following the quantification of total RNA concentrations, the PrimeScript™ II 1st Strand cDNA Synthesis kit (Takara, Bio, Inc.) was used to generate cDNA. A SYBR Green PCR master mix kit (SYBR® Premix Ex Taq™-Tli RNaseH Plus; Takara, Bio, Inc.) was used for qPCR. The thermocycling conditions were as follows: 95°C for 30 sec; 40 cycles at 95°C for 5 sec, 60°C for 30 sec and 72°C for 30 sec. mRNA relative expression levels were quantified using the 2−ΔΔCq method (30) and normalized to GAPDH. The following primers were used: MMP2 forward, 5′-TGACATACATCTTTGCTGGAGAC-3′ and reverse, 5′-GGCTTGCGAGGGAAGAAGTT-3′; GAPDH forward, 5′-TTCAGGTAATAGGCACCCTT-3′ and reverse, 5′-CTTCTCCATGGTGGTGAAGA-3′.
Cell migration assay
A migration assay was performed using Transwell inserts. Cells were maintained at a concentration of 4×105 cells/ml in serum-free RPMI-1640. A total of 300 µl cell suspension was added into the upper chamber, whilst the lower chamber was treated with 600 µl of RPMI-1640 with 10% FBS. Following incubation at 37°C for 24 h, the medium was discarded and non-migrating cells on the top surface of the upper chamber were removed gently using cotton swabs. Migrated cells were fixed with pre-chilled methanol for 30 min then stained with 0.5% crystal violet at room temperature for 20 min. Representative images were taken under an inverted microscope (magnification, ×10 and ×20) equipped with a camera (Leica Microsystems GmbH). Subsequently, 33% glacial acetic acid (200 µl) was added for 10 min to de-stain. Absorbance was measured at 570 nm using a microplate reader.
Cell invasion assay
For the invasion assay, the upper chamber was pre-coated with Matrigel. Ice-cold Matrigel was mixed with ice-cold RPMI-1640 medium at a ratio of 1:1 and spread onto the upper chamber (50 µl/chamber), which was subsequently incubated at 37°C for 2 h. The following steps including cell plating, incubation, fixing and de-staining were conducted as aforementioned for the migration assay. Representative images were taken under an inverted microscope (magnification, ×10 and ×20) equipped with a camera (Leica Microsystems GmbH).
Statistical analysis
Statistical analysis was performed using SPSS v13.0 (SPSS, Inc.). Data were presented as the mean ± standard deviation based on at least three replicates. The differences among groups were analyzed using one-way analysis of variance followed by Least Significant Difference post-hoc test. P<0.05 was considered to indicate statistical significance.
Results
Cd treatment at the highest concentration decreases A549 cell viability
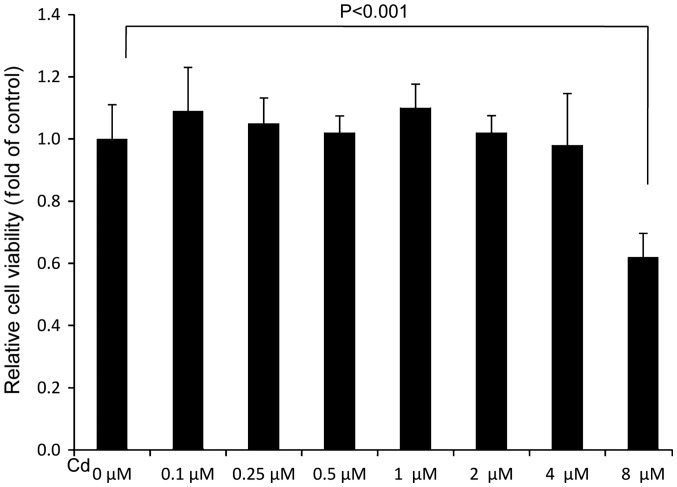
To assess the effect of Cd treatment on cell viability, an MTT assay was performed. The results revealed that the relative cell viability of the 8 µM Cd treatment group was significantly lower than the solvent control (0 µM), indicating that 8 µM Cd had a marked cytotoxic effect (Fig. 1). Cd treatment demonstrated no marked effect on cell viability when the concentration was <4 µM (Fig. 1).
Figure 1.
Effects of Cd treatment on A549 cell viability. A549 cells were treated with the indicated concentrations of Cd for 48 h. An MTT assay was subsequently performed. Relative cell viability was determined by normalizing to the control (0 µM). Cd, cadmium.
Cd treatment increases the expression of p-ERK in A549 cells
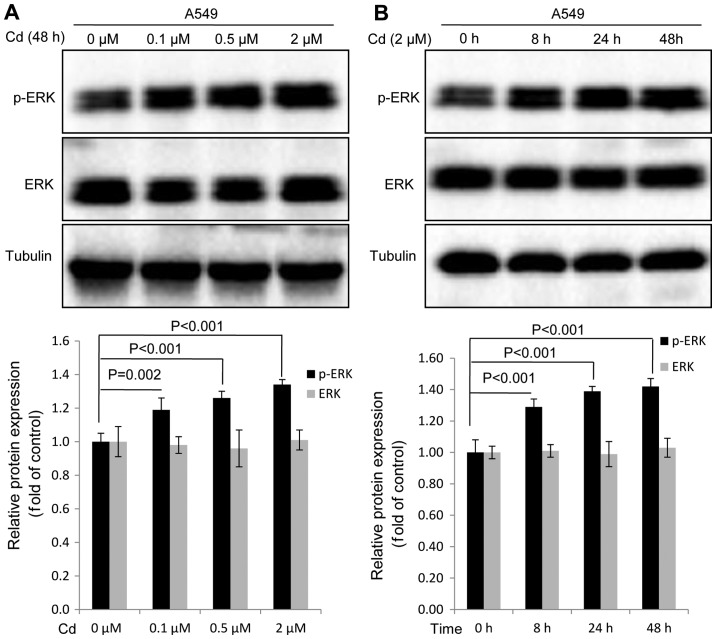
Western blot analysis was conducted to investigate whether Cd affected the expression of p-ERK in A549 cells. The results revealed that the expression of p-ERK was markedly increased in a dose-dependent manner when A549 cells were treated with Cd for 48 h (Fig. 2A). When compared with the 0 h group, a significant increase in p-ERK expression was observed when A549 cells were treated with 2 µM Cd for increasing time durations (Fig. 2B). Cd treatment exhibited no effect on the expression of total ERK protein (Fig. 2). The results indicated that ERK activation was induced by Cd treatment.
Figure 2.
Effects of Cd treatment on p-ERK protein expression. (A) Western blot analysis to measure the expression of p-ERK protein following treatment with indicated concentrations of Cd for 48 h or (B) 2 µM Cd for 8, 24 or 48 h. P<0.05 was considered to indicate a statistically significant difference. Cd, cadmium; p, phosphorylated.
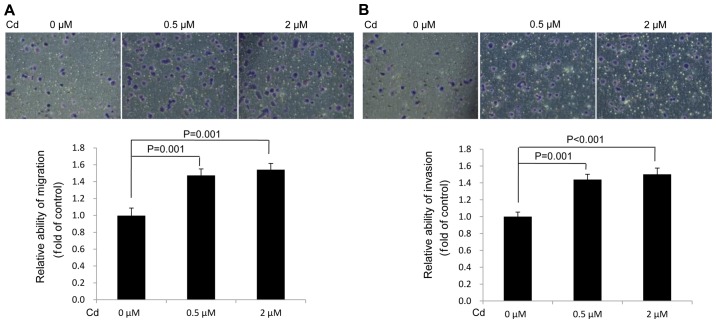
Cd accelerates the migration and invasion of A549 cells
The data demonstrated that Cd treatment increased A549 cell migration (Fig. 3A) and invasion (Fig. 3B) compared with the solvent control (0 µM). The results verified that Cd treatment facilitated the migration and invasion of A549 cells.
Figure 3.
Effects of Cd treatment on A549 cell migration and invasion. (A) Relative cell migration and (B) invasion were quantified as the fold change with respect to the control (magnification, ×200). Cd, cadmium.
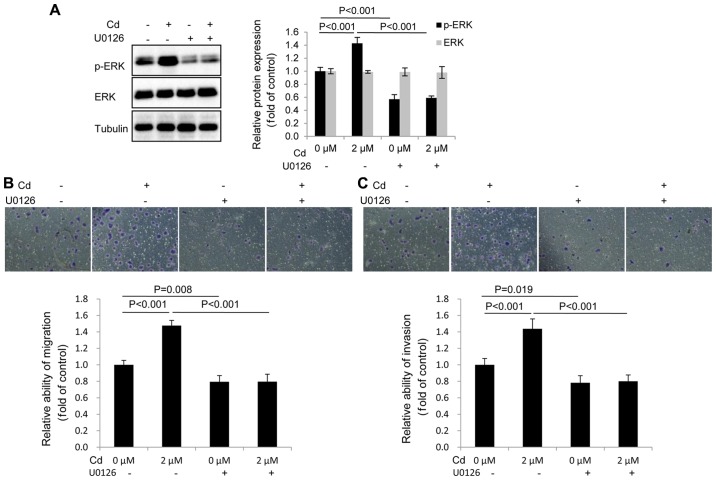
p-ERK has an important role in the migration and invasion of A549 cells following Cd treatment
The migration and invasion of A549 cells were assessed following pretreatment with 10 µM U0126 (an inhibitor of MEK1/2), followed by 2 µM Cd treatment. The results revealed that the expression of p-ERK was markedly decreased in the U0126-treated group compared with the control group (Fig. 4A). In addition, U0126 blocked the expression of p-ERK following Cd treatment. The data therefore demonstrated that U0126 effectively inhibited the expression of p-ERK (Fig. 4A). It was also determined that U0126 inhibited the migration and invasion of A549 cells following Cd treatment (Fig. 4B and C), indicating that elevated p-ERK activity was required for Cd-induced migration and invasion.
Figure 4.
p-ERK has an important role in the Cd-induced migration and invasion of A549 cells. (A) Western blot analysis was conducted to measure the expression of p-ERK in the presence of 2 µM Cd and 10 µM U0126. (B) Migration and (C) invasion assays were performed in the presence of 2 µM Cd and 10 µM U0126, and quantified as the fold change with respect to the control (magnification, ×200). Cd, cadmium; p, phosphorylated.
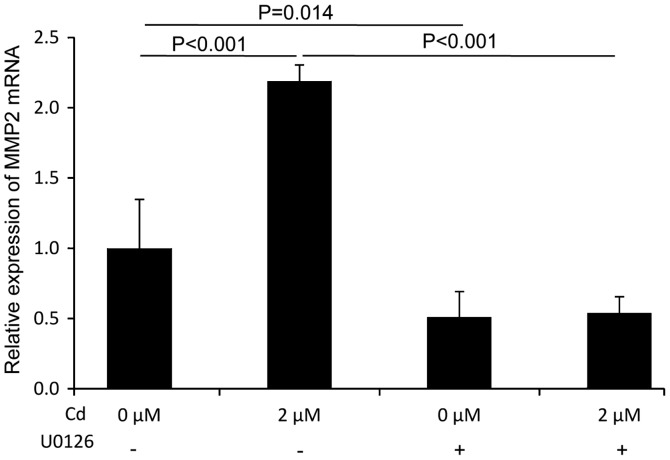
MMP2 mRNA expression following Cd treatment is mediated by p-ERK
An investigation into whether MMP2 was a downstream signaling molecule in the ERK pathway was performed using RT-qPCR. The results revealed that Cd treatment significantly increased the expression of MMP2 mRNA compared with the control group. Furthermore, the Cd-induced expression of MMP2 mRNA was significantly suppressed in the presence of U0126 (Fig. 5). These results indicated that MMP2 mRNA expression was modulated by p-ERK following Cd treatment and also that MMP2 might be a downstream molecule in the ERK signaling pathway.
Figure 5.
MMP2 mRNA expression induced by Cd is modulated by p-ERK in A549 cells. Reverse transcription-quantitative PCR was performed to detect the mRNA expression of MMP2 in A549 cells in the presence of 2 µM Cd and 10 µM U0126. MMP, matrix metalloproteinase; Cd, cadmium; p, phosphorylated.
Discussion
Cd is a widely used heavy metal environmental pollutant. Previous studies have identified that exposure to Cd is closely associated with the progression of various types of cancer. He et al (31) reported that blood Cd levels are positively associated with distant metastasis and clinical stage of human breast cancer. Demir et al (32) demonstrated that Cd levels in tumor tissue are significantly correlated with lung cancer TNM staging. Furthermore, Son et al (33) reported that chronic Cd treatment enhanced cell migration and invasion in BEAS-2B cells and increased tumor growth in a mouse xenograft model. Person et al (7) also determined that chronic Cd-treated lung cells exhibit a marked increase in invasion compared with control cells. Wei and Shaikh (34) reported that increased cell migration and invasion is demonstrated in prolonged Cd-treated triple-negative breast cancer cells. Finally, Zhu et al (12) demonstrated that migration and invasion is induced in human follicular WRO and anaplastic FRO thyroid cancer cells when treated with Cd at 250–1,000 nM.
Currently, three published articles have demonstrated that exposure to Cd induces migration and invasion of lung cancer cells. Luo et al (10) demonstrated that treatment with Cd increased the expression of certain invasion-associated proteins in the lung tissue of mice and in A549 cells, including MMP9, MMP2 and p-protein tyrosine kinase 2. The study also revealed that high-mobility group AT-hook (HMGA2) serves a significant role in Cd-induced A549 cell migration and invasion (10). Lv et al (11) reported that Cd markedly enhances cell proliferation, migration and invasion in lung cancer A549 cells. It was also determined that reactive oxygen species-dependent autophagy and related 4A cysteine peptidase upregulation-mediated autophagy may affect Cd-induced cell growth, migration and invasion. Fujiki et al (35) demonstrated that prolonged Cd exposure induced epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT), stress-fiber formation and high cell motility in A549 cells, which was partially suppressed by small interfering RNA-mediated Notch1 silencing. These studies indicated that Cd promoted lung cancer cell migration and invasion via different mechanisms.
ERK is activated on both the Thr202 and Tyr204 residues via sequential phosphorylation cascades. It also regulates several downstream events, such as cell proliferation, differentiation, motility and cell death (36–38). It has been reported that the ERK signaling pathway is involved in cell migration and invasion in several types of cancer cell. Peng et al (39) reported that anti-migration and anti-invasion activities of oxyfadichalcone C were associated with the downregulation of the MAPK/ERK signaling pathways in melanoma A375 cells. Wang et al (40) reported that the chrysin-induced inhibition of proliferation, migration and invasion in glioblastoma cells was mediated by the ERK/Nrf2 signaling pathway. Additionally, Hong et al (41) reported that microRNA-508 suppresses the EMT, migration and invasion of ovarian cancer cells via the MAPK1/ERK signaling pathway. Li et al (42) also reported that microRNA-23a promoted cell growth and metastasis in gastric cancer by targeting sprouty RTK signaling antagonist 2-mediated ERK signaling. A previous study demonstrated that p-ERK serves an important role in benzo(a)pyrene-induced Hep-G2 cell migration and invasion (14).
MMP2, a member of the extracellular matrix degrading proteinase family, is vital for the promotion of tumor metastasis. Previous studies have determined that MMP2 is implicated in the migration and invasion of lung cancer cells. Dong et al (43) reported that the inhibition of cell invasion occurs as a result of decreased MMP2 levels in NSCLC cell lines. In addition, it has been reported that MMP2 is a downstream molecule of the ERK pathway. For example, Wu et al (44) determined that MMP2 was mediated by the ERK signaling pathway potentially via microfibrillar-associated protein 5, which was associated with tissue development and cancer progression. Furthermore, Li et al (45) reported that the activation of the ERK/NF-κB signaling pathway promoted the expression of MMP2 and induced cell migration and invasion. Yu et al (46) also reported that andrographolide enhanced the anti-metastatic effect of radiation in Ras-transformed cells by suppressing ERK-mediated MMP2 activity. Yang et al (47) demonstrated that andrographolide suppressed the migratory ability of human glioblastoma multiforme cells by targeting ERK1/2-mediated MMP2 expression.
U0126 is a highly selective inhibitor of MEK1 (IC50, 72 nM) and MEK2 (IC50, 58 nM; a type of MAPK/ERK kinase) (48), and is also a weak inhibitor of proline rich transmembrane protein 2, Raf, JNK, mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase kinase 1, mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase (MKK) 3, MKK-4/EPH receptor A4, MKK-6, cyclin-dependent kinase (Cdk)-2 and Cdk4. Micromolar concentrations of U0126 were used to inhibit ERK1/2 activation in previous studies, including 5 (29), 20 (49) and 40 µM (26). As the most commonly used U0126 concentration (27,29,50,51), 10 µM U0126 was selected in the present study to inhibit the activation of ERK1/2.
The present study investigated the effects of Cd on the migration and invasion of A549 cells as well as the potential role of p-ERK in Cd-induced cell migration and invasion. The results demonstrated that Cd-treated lung cancer A549 cell migration and invasion increased compared with the control. Migration and invasion were also decreased when cells were pre-treated with U0126, an inhibitor of MEK1/2. Data also indicated that p-ERK served an important role in Cd-induced A549 cell migration and invasion. In addition, RT-qPCR determined that the Cd-induced expression of MMP2 mRNA was significantly reduced in the presence of U0126, which indicated that MMP2 might be a downstream molecule in the ERK signaling pathway. Further investigation should be performed to confirm the pattern of A549 cell MMP2 protein expression and activity in the presence of Cd and U0126.
HMGA2 is a driver of tumor cell migration, invasion and metastasis (52–54) and there is a proven link between HMGA2 and p-ERK. Hawsawi et al (55) demonstrated that HMGA2 promoted EMT via the MAPK/ERK signaling pathway in prostate cancer. Ping et al (56) also reported that angiotensin II type 2 receptor-interacting protein 3a presented potential in suppressing the proliferation and aggressiveness of ovarian carcinoma cells via the HMGA2-mediated ERK/EMT signaling pathway. Additionally, Kao et al (57) indicated that Hsp90 indirectly regulated HMGA2 by activating the ERK signaling pathway. HMGA2 upregulation is mediated by Cd-induced A549 cell migration and invasion (10). The present study determined that ERK activation was involved in Cd-induced A549 cell migration and invasion. However, the link between HMGA2 and p-ERK in Cd-induced A549 cell migration and invasion was not investigated and will be the focus of future studies.
To the best of our knowledge, the present study demonstrated for the first time that Cd induced A549 cell migration and invasion by activating the ERK-MMP2 pathway. The results may contribute to the further understanding of the molecular mechanisms of Cd-induced lung-cancer cell migration and invasion, and provide insight to potentially improve lung cancer treatment caused by environmental Cd.
Acknowledgements
Not applicable.
Funding
The current study was funded by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (grant no. U1404815) and Henan Province University Science and Technology Innovation Talent Projects (grant no. 17HASTIT045). The funder had no role in the study design, data collection and analysis, decision to publish, or preparation of the manuscript.
Availability of data and materials
The datasets generated and/or analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
Authors' contributions
YW and HY designed and implemented the current study, performed the experiments and analyzed the data. TP and HZ performed western blotting and RT-qPCR analysis. YW, HZ and HW performed the MTT, migration and invasion assays. HZ and YW wrote the manuscript.
Ethics approval and consent to participate
Not applicable.
Patient consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
References
- 1.Torre LA, Bray F, Siegel RL, Ferlay J, Lortet-Tieulent J, Jemal A. Global cancer statistics, 2012. CA Cancer J Clin. 2015;65:87–108. doi: 10.3322/caac.21262. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Nawrot TS, Martens DS, Hara A, Plusquin M, Vangronsveld J, Roels HA, Staessen JA. Association of total cancer and lung cancer with environmental exposure to cadmium: The meta-analytical evidence. Cancer Causes Control. 2015;26:1281–1288. doi: 10.1007/s10552-015-0621-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Verma M. Environmental and occupational risk factors for lung cancer, methods of molecular biology. Cancer Epidemiol. 2009;472:3–23. doi: 10.1007/978-1-60327-492-0_1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Garcia-Esquinas E, Pollan M, Tellez-Plaza M, Francesconi KA, Goessler W, Guallar E, Umans JG, Yeh J, Best LG, Navas-Acien A. Cadmium exposure and cancer mortality in a prospective cohort: The strong heart study. Environ Health Perspect. 2014;122:363–370. doi: 10.1289/ehp.1306587. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Stayner L, Smith R, Thun M, Schnorr T, Lemen R. A dose-response analysis and quantitative assessment of lung cancer risk and occupational cadmium exposure. Ann Epidemiol. 1992;2:177–194. doi: 10.1016/1047-2797(92)90052-R. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Meeting of the IARC working group on beryllium, cadmium, mercury and exposures in the glass manufacturing industry. Scand J Work Environ Health. 1993;19:360–363. doi: 10.5271/sjweh.1461. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Person RJ, Tokar EJ, Xu Y, Orihuela R, Ngalame NN, Waalkes MP. Chronic cadmium exposure in vitro induces cancer cell characteristics in human lung cells. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 2013;273:281–288. doi: 10.1016/j.taap.2013.06.013. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Huff J, Lunn RM, Waalkes MP, Tomatis L, Infante PF. Cadmium-induced cancers in animals and in humans. Int J Occup Environ Health. 2007;13:202–212. doi: 10.1179/oeh.2007.13.2.202. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Luevano J, Damodaran C. A review of molecular events of cadmium-induced carcinogenesis. J Environ Pathol Toxicol Oncol. 2014;33:183–194. doi: 10.1615/JEnvironPatholToxicolOncol.2014011075. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Luo H, Li Z, Ge H, Mei D, Zhao L, Jiang L, Geng C, Li Q, Yao X, Cao J. HMGA2 upregulation mediates Cd-induced migration and invasion in A549 cells and in lung tissues of mice. Chem Biol Interact. 2017;277:1–7. doi: 10.1016/j.cbi.2017.08.012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Lv W, Sui L, Yan X, Xie H, Jiang L, Geng C, Li Q, Yao X, Kong Y, Cao J. ROS-dependent Atg4 upregulation mediated autophagy plays an important role in Cd-induced proliferation and invasion in A549 cells. Chem Biol Interact. 2018;279:136–144. doi: 10.1016/j.cbi.2017.11.013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Zhu P, Liao LY, Zhao TT, Mo XM, Chen GG, Liu ZM. GPER/ERK&AKT/NF-κB pathway is involved in cadmium-induced proliferation, invasion and migration of GPER-positive thyroid cancer cells. Mol Cell Endocrinol. 2017;442:68–80. doi: 10.1016/j.mce.2016.12.007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Wei Y, Zhao L, He W, Yang J, Geng C, Chen Y, Liu T, Chen H, Li Y. Benzo[a]pyrene promotes gastric cancer cell proliferation and metastasis likely through the Aryl hydrocarbon receptor and ERK-dependent induction of MMP9 and c-myc. Int J Oncol. 2016;49:2055–2063. doi: 10.3892/ijo.2016.3674. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Wang Y, Pan T, Li L, Wang H, Zhang D, Yang H. Benzo(a)pyrene promotes Hep-G2 cell migration and invasion by upregulating phosphorylated extracellular signal-regulated kinase expression. Oncol Lett. 2018;15:8325–8332. doi: 10.3892/ol.2018.8379. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Sharma K, Singh J, Frost EE, Pillai PP. MeCP2 overexpression inhibits proliferation, migration and invasion of C6 glioma by modulating ERK signaling and gene expression. Neurosci Lett. 2018;674:42–48. doi: 10.1016/j.neulet.2018.03.020. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Sun Y, Lan M, Chen X, Dai Y, Zhao X, Wang L, Zhao T, Li Y, Zhu J, Zhang X, et al. Anti-invasion and anti-metastasis effects of Valjatrate E via reduction of matrix metalloproteinases expression and suppression of MAPK/ERK signaling pathway. Biomed Pharmacother. 2018;104:817–824. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2018.04.136. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Quintero Barceinas RS, Garcia-Regalado A, Arechaga- Ocampo E, Villegas-Sepulveda N, Gonzalez-De la Rosa CH. All-Trans retinoic acid induces proliferation, survival, and migration in A549 lung cancer cells by activating the ERK signaling pathway through a transcription-independent mechanism. Biomed Res Int. 2015;2015:404368. doi: 10.1155/2015/404368. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Li G, He Y, Yao J, Huang C, Song X, Deng Y, Xie S, Ren J, Jin M, Liu H. Angelicin inhibits human lung carcinoma A549 cell growth and migration through regulating JNK and ERK pathways. Oncol Rep. 2016;36:3504–3512. doi: 10.3892/or.2016.5166. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Tang F, Tang S, Guo X, Yang C, Jia K. CT45A1 siRNA silencing suppresses the proliferation, metastasis and invasion of lung cancer cells by downregulating the ERK/CREB signaling pathway. Mol Med Rep. 2017;16:6708–6714. doi: 10.3892/mmr.2017.7466. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Zhang X, Zhang Y, Miao Y, Zhou H, Jiang G, Wang E. TMEM17 depresses invasion and metastasis in lung cancer cells via ERK signaling pathway. Oncotarget. 2017;8:70685–70694. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.19977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Yang J, Kuang XR, Lv PT, Yan XX. Thymoquinone inhibits proliferation and invasion of human nonsmall-cell lung cancer cells via ERK pathway. Tumour Biol. 2015;36:259–269. doi: 10.1007/s13277-014-2628-z. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Liao YC, Shih YW, Chao CH, Lee XY, Chiang TA. Involvement of the ERK signaling pathway in fisetin reduces invasion and migration in the human lung cancer cell line A549. J Agric Food Chem. 2009;57:8933–8941. doi: 10.1021/jf902630w. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Shih YW, Wu PF, Lee YC, Shi MD, Chiang TA. Myricetin suppresses invasion and migration of human lung adenocarcinoma A549 cells: Possible mediation by blocking the ERK signaling pathway. J Agric Food Chem. 2009;57:3490–3499. doi: 10.1021/jf900124r. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Kim JH, Cho EB, Lee J, Jung O, Ryu BJ, Kim SH, Cho JY, Ryou C, Lee SY. Emetine inhibits migration and invasion of human non-small-cell lung cancer cells via regulation of ERK and p38 signaling pathways. Chem Biol Interact. 2015;242:25–33. doi: 10.1016/j.cbi.2015.08.014. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Wang Y, Wang H, Pan T, Li L, Li J, Yang H. STIM1 silencing inhibits the migration and invasion of A549 cells. Mol Med Rep. 2017;16:3283–3289. doi: 10.3892/mmr.2017.7010. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Zhu X, Price-Schiavi SA, Carraway KL. Extracellular regulated kinase (ERK)-dependent regulation of sialomucin complex/rat Muc4 in mammary epithelial cells. Oncogene. 2000;19:4354–4361. doi: 10.1038/sj.onc.1203781. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Wang X, Martindale JL, Holbrook NJ. Requirement for ERK activation in cisplatin-induced apoptosis. J Biol Chem. 2000;275:39435–39443. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M004583200. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Silvany RE, Eliazer S, Wolff NC, Ilaria RL., Jr Interference with the constitutive activation of ERK1 and ERK2 impairs EWS/FLI-1-dependent transformation. Oncogene. 2000;19:4523–4530. doi: 10.1038/sj.onc.1203811. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Raja R, Lata S, Trivedi S, Banerjea AC. Serum deprivation/starvation leads to reactivation of HIV-1 in latently infected monocytes via activating ERK/JNK pathway. Sci Rep. 2018;8:14496. doi: 10.1038/s41598-018-32316-2. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Livak KJ, Schmittgen TD. Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 2001;25:402–408. doi: 10.1006/meth.2001.1262. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.He Y, Peng L, Huang Y, Liu C, Zheng S, Wu K. Blood cadmium levels associated with short distant metastasis-free survival time in invasive breast cancer. Environ Sci Pollut Res Int. 2017;24:28055–28064. doi: 10.1007/s11356-017-0412-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Demir N, Enon S, Turksoy VA, Kayaalti Z, Kaya S, Cangir AK, Soylemezoglu T, Savas I. Association of cadmium but not arsenic levels in lung cancer tumor tissue with smoking, histopathological type and stage. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev. 2014;15:2965–2970. doi: 10.7314/APJCP.2014.15.7.2965. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Son YO, Wang L, Poyil P, Budhraja A, Hitron JA, Zhang Z, Lee JC, Shi X. Cadmium induces carcinogenesis in BEAS-2B cells through ROS-dependent activation of PI3K/AKT/GSK-3β/β- catenin signaling. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 2012;264:153–160. doi: 10.1016/j.taap.2012.07.028. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Wei Z, Shaikh ZA. Cadmium stimulates metastasis-associated phenotype in triple-negative breast cancer cells through integrin and β-catenin signaling. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 2017;328:70–80. doi: 10.1016/j.taap.2017.05.017. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Fujiki K, Inamura H, Miyayama T, Matsuoka M. Involvement of Notch1 signaling in malignant progression of A549 cells subjected to prolonged cadmium exposure. J Biol Chem. 2017;292:7942–7953. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M116.759134. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Eblen ST. Extracellular-regulated kinases: Signaling from ras to ERK substrates to control biological outcomes. Adv Cancer Res. 2018;138:99–142. doi: 10.1016/bs.acr.2018.02.004. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Tanimura S, Takeda K. ERK signalling as a regulator of cell motility. J Biochem. 2017;162:145–154. doi: 10.1093/jb/mvx048. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Sun Y, Liu WZ, Liu T, Feng X, Yang N, Zhou HF. Signaling pathway of MAPK/ERK in cell proliferation, differentiation, migration, senescence and apoptosis. J Recept Signal Transduct Res. 2015;35:600–604. doi: 10.3109/10799893.2015.1030412. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Peng X, Wang Z, Liu Y, Peng X, Liu Y, Zhu S, Zhang Z, Qiu Y, Jin M, Wang R, et al. Oxyfadichalcone C inhibits melanoma A375 cell proliferation and metastasis via suppressing PI3K/Akt and MAPK/ERK pathways. Life Sci. 2018;206:35–44. doi: 10.1016/j.lfs.2018.05.032. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Wang J, Wang H, Sun K, Wang X, Pan H, Zhu J, Ji X, Li X. Chrysin suppresses proliferation, migration, and invasion in glioblastoma cell lines via mediating the ERK/Nrf2 signaling pathway. Drug Des Devel Ther. 2018;12:721–733. doi: 10.2147/DDDT.S160020. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Hong L, Wang Y, Chen W, Yang S. MicroRNA-508 suppresses epithelial-mesenchymal transition, migration, and invasion of ovarian cancer cells through the MAPK1/ERK signaling pathway. J Cell Biochem. 2018;119:7431–7440. doi: 10.1002/jcb.27052. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.Li Y, Chen H, She P, Chen T, Chen L, Yuan J, Jiang B. microRNA-23a promotes cell growth and metastasis in gastric cancer via targeting SPRY2-mediated ERK signaling. Oncol Lett. 2018;15:8433–8441. doi: 10.3892/ol.2018.8374. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar] [Retracted]
- 43.Dong QZ, Wang Y, Tang ZP, Fu L, Li QC, Wang ED, Wang EH. Derlin-1 is overexpressed in non-small cell lung cancer and promotes cancer cell invasion via EGFR-ERK-mediated up-regulation of MMP-2 and MMP-9. Am J Pathol. 2013;182:954–964. doi: 10.1016/j.ajpath.2012.11.019. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44.Wu Z, Wang T, Fang M, Huang W, Sun Z, Xiao J, Yan W. MFAP5 promotes tumor progression and bone metastasis by regulating ERK/MMP signaling pathways in breast cancer. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2018;498:495–501. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2018.03.007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45.Li X, Bao C, Ma Z, Xu B, Liu X, Ying X, Zhang X. Perfluorooctanoic acid stimulates ovarian cancer cell migration, invasion via ERK/NF-κB/MMP-2/-9 pathway. Toxicol Lett. 2018;294:44–50. doi: 10.1016/j.toxlet.2018.05.009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 46.Yu CC, Chen CA, Fu SL, Lin HY, Lee MS, Chiou WY, Su YC, Hung SK. Andrographolide enhances the anti-metastatic effect of radiation in Ras-transformed cells via suppression of ERK-mediated MMP-2 activity. PLoS One. 2018;13:e0205666. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0205666. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 47.Yang SL, Kuo FH, Chen PN, Hsieh YH, Yu NY, Yang WE, Hsieh MJ, Yang SF. Andrographolide suppresses the migratory ability of human glioblastoma multiforme cells by targeting ERK1/2-mediated matrix metalloproteinase-2 expression. Oncotarget. 2017;8:105860–105872. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.22407. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 48.Favata MF, Horiuchi KY, Manos EJ, Daulerio AJ, Stradley DA, Feeser WS, Van Dyk DE, Pitts WJ, Earl RA, Hobbs F, et al. Identification of a novel inhibitor of mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase. J Biol Chem. 1998;273:18623–18632. doi: 10.1074/jbc.273.29.18623. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 49.Gao H, Zhang Y, Dong L, Qu XY, Tao LN, Zhang YM, Zhai JH, Song YQ. Triptolide induces autophagy and apoptosis through ERK activation in human breast cancer MCF-7 cells. Exp Ther Med. 2018;15:3413–3419. doi: 10.3892/etm.2018.5830. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 50.Jiang X, Li H. Overexpression of LRIG1 regulates PTEN via MAPK/MEK signaling pathway in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Exp Ther Med. 2016;12:2045–2052. doi: 10.3892/etm.2016.3606. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 51.Yang Y, Gong L. Palmitoleate inhibits insulin transcription by activating the ERK1/2 pathway in rat pancreatic beta-cells. Exp Ther Med. 2017;13:2805–2811. doi: 10.3892/etm.2017.4344. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 52.Morishita A, Zaidi MR, Mitoro A, Sankarasharma D, Szabolcs M, Okada Y, D'Armiento J, Chada K. HMGA2 is a driver of tumor metastasis. Cancer Res. 2013;73:4289–4299. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-12-3848. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 53.Gao X, Dai M, Li Q, Wang Z, Lu Y, Song Z. HMGA2 regulates lung cancer proliferation and metastasis. Thoracic Cancer. 2017;8:501–510. doi: 10.1111/1759-7714.12476. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 54.Dong J, Wang R, Ren G, Li X, Wang J, Sun Y, Liang J, Nie Y, Wu K, Feng B, et al. HMGA2-FOXL2 axis regulates metastases and epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition of chemoresistant gastric cancer. Clin Cancer Res. 2017;23:3461–3473. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-16-2180. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 55.Hawsawi O, Henderson V, Burton LJ, Dougan J, Nagappan P, Odero-Marah V. High mobility group A2 (HMGA2) promotes EMT via MAPK pathway in prostate cancer. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2018;504:196–202. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2018.08.155. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 56.Ping H, Guo L, Xi J, Wang D. Angiotensin II type 2 receptor-interacting protein 3a inhibits ovarian carcinoma metastasis via the extracellular HMGA2-mediated ERK/EMT pathway. Tumour Biol. 2017;39:1010428317713389. doi: 10.1177/1010428317713389. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 57.Kao CY, Yang PM, Wu MH, Huang CC, Lee YC, Lee KH. Heat shock protein 90 is involved in the regulation of HMGA2-driven growth and epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition of colorectal cancer cells. PeerJ. 2016;4:e1683. doi: 10.7717/peerj.1683. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Data Availability Statement
The datasets generated and/or analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.