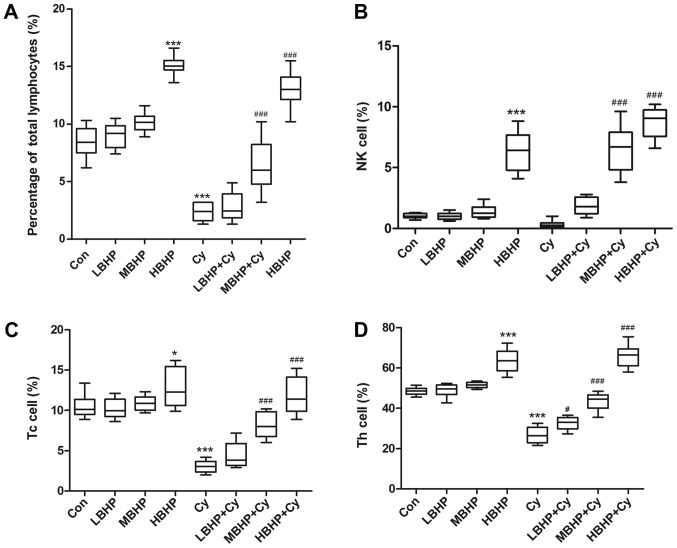
Figure 2.
Percentages of lymphocytes in normal untreated mice and normal and immunosuppressed mice treated with BHP. (A) Percentages of total lymphocytes were increased in the HBHP group and significantly decreased in the Cy group compared with that in the Con group, and were increased significantly in the MBHP + Cy and HBHP + Cy groups compared with that in the Cy group. (B) Percentages of NK cells. NK cell percentage was increased significantly in the HBHP group compared with that in the Con group. NK cell percentages were increased significantly in the MBHP + Cy and HBHP + Cy groups compared with that in the Cy group. (C) Percentages of Tc cells. Tc cell percentage was increased in the HBHP group and significantly decreased in the Cy group compared with that in the Con group. Percentages of Tc cells were increased significantly in the MBHP + Cy and HBHP + Cy groups compared with that in the Cy group. (D) Percentage of Th cells was increased in the HBHP group and significantly decreased in the Cy group compared with that in the Con group. Percentages of Th cells were increased significantly in the LBHP + Cy, MBHP + Cy and HBHP + Cy groups compared with that in the Cy group. *P<0.01 vs. Con group; ***P<0.0001 vs. Con group; #P<0.01 vs. Cy group; ###P<0.0001 vs. Cy group. All data were from two independent experiments, each of which was repeated in parallel twice. BHP, bioactive hepatic peptide; LBHP, low-dose BHP; MBHP, mid-dose BHP; HBHP, high-dose BHP; Cy, cyclophosphamide; Con, control; NK, natural killer; Tc, cytotoxic T cell; Th, T helper cell.