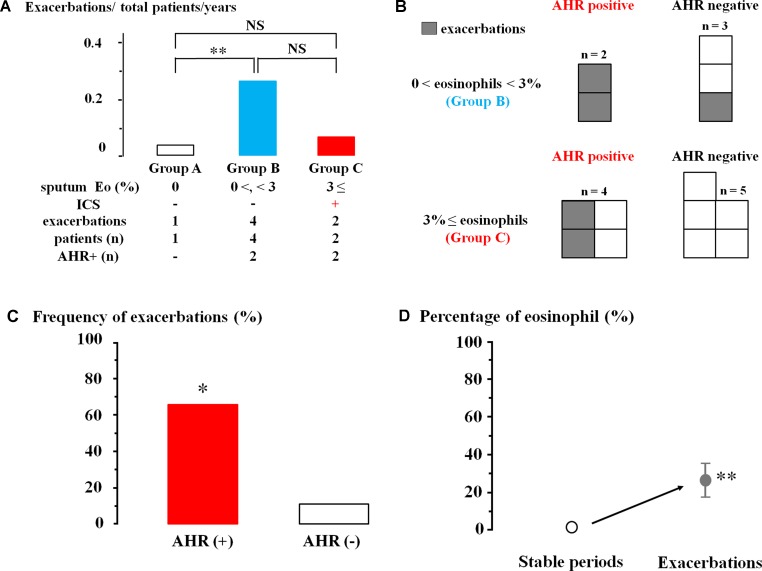
Figure 5.
Involvement of airway eosinophilia, airway hyperresponsiveness, and ICS in occurrence of exacerbations of chronic obstructive lung disease (COPD). (A) Frequency of exacerbations of COPD in sputum eosinophils 0% without ICS (Group A, white column), 0% < sputum eosinophils < 3% without ICS (Group B, blue column), and sputum eosinophils ≥3% with ICS (Group C, red column). (B) The number of patients with exacerbations in those who underwent acetylcholine provocation test in Groups B and C. (C) Frequency of exacerbations in COPD with AHR and without AHR in Groups B and C. (D) Mean values of the percentages of sputum eosinophils in stable periods and exacerbations. AHR, airway hyperresponsiveness; ICS, inhaled glucocorticosteroid. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, NS, not significant.