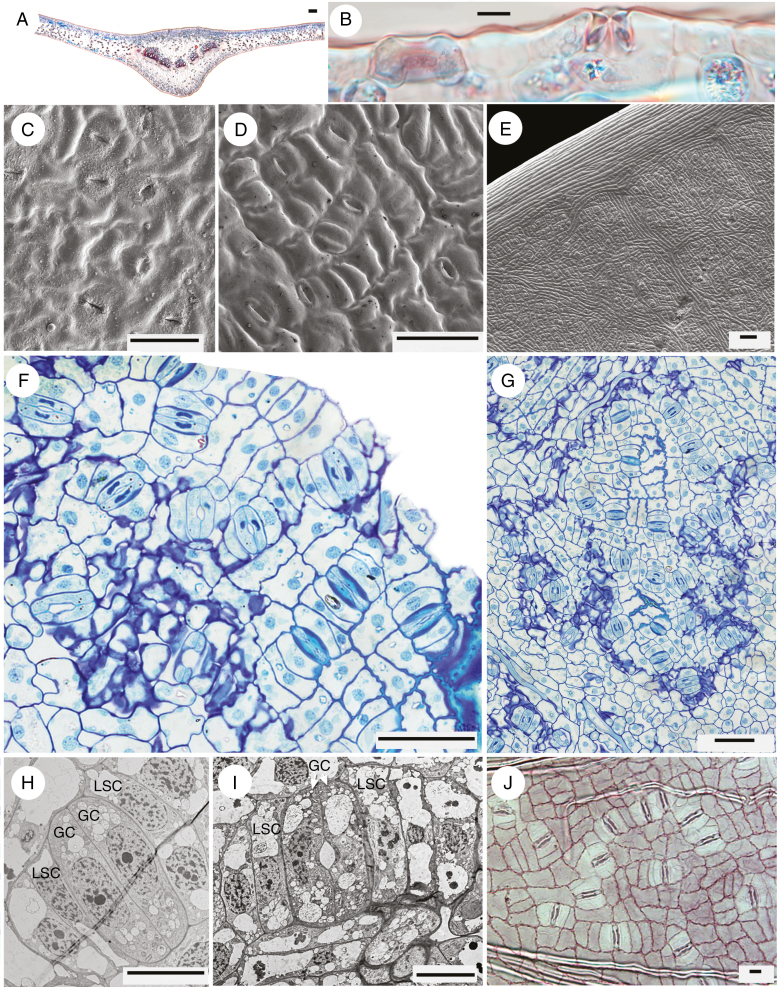
Fig. 5.
Gnetum gnemon. (A) Transverse section of leaf (from a slide in Kew’s microscope slide collection). (B) Detail of abaxial epidermis in transverse section, showing two stomata, one perpendicular to the other. (C) Abaxial surface of mature leaf encrusted with surface waxes; stomatal guard cells slightly raised (SEM). (D) Abaxial surface of younger leaf showing regular stomatal orientation (SEM). (E) Abaxial leaf surface showing margin and areoles between veins (SEM). (F, G) Abaxial epidermis of mature leaf showing mostly regular stomatal orientation. (H, I) Mature stomata showing lateral subsidiary cells adjacent to guard cells (TEM). (J) Abaxial epidermis of mature leaf (from a slide in Kew’s microscope slide collection). Scale bars: (A, E) = 100 μm; (B, H–J) = 10 μm; (C, D, F, G) = 50 μm. GC, guard cell, LSC, lateral subsidiary cell.