Figure 4: Evaluation of RBP motifs by allelic protein-RNA interactions.
Related to Figures S4 and S5.
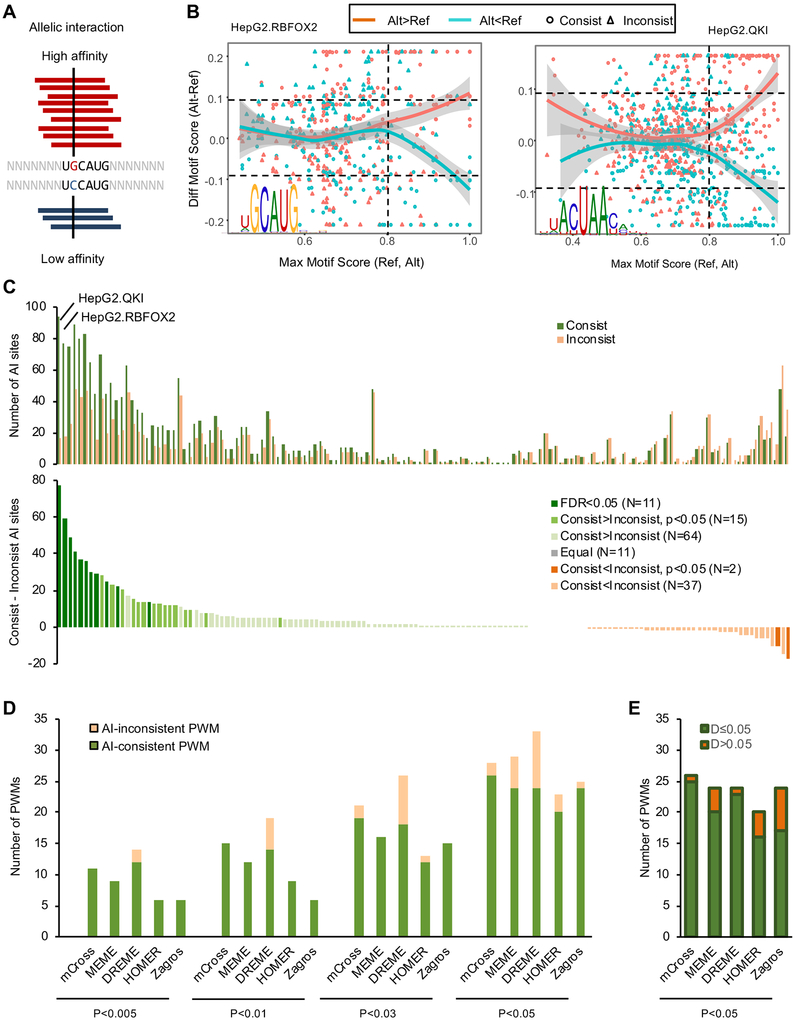
(A) Schematic of a heterozygous SNP affecting Rbfox binding and the resulting allelic imbalance in eCLIP data.
(B) The relationship between the allelic bias of CLIP tags and the motif scores of the reference and alternative alleles overlapping with SNPs using RBFOX2 and QKI eCLIP in HepG2 cells are shown for examples. In each panel, each dot represents a SNP with significant allelic imbalance in CLIP data. SNPs with more alternative allele tags are shown in red and those with more reference allele tags are shown in cyan. X-axis shows the maximum motif score for either the reference or alternative allele of all positions overlapping with the SNP, measuring the likelihood of RBP binding at least one allele. Y-axis shows the difference of the maximum motif score among all positions overlapping with the alternative allele and the maximum motif score among all positions overlapping with the reference allele, measuring the impact of the SNP on RBP binding. SNPs with consistent allelic bias in CLIP tags and motif score changes are shown in circles while inconsistent SNPs are shown in triangles.
(C) The number of consistent and inconsistent AI SNP sites for each RBP (top). For this analysis, the top PWM was used as a representative for each RBP. The excess of consistent over inconsistent AI sites is shown at the bottom and RBPs are color-coded based on the extent of excess using a Binomial test.
(D) Comparison of mCross and other de novo motif discovery programs using eCLIP data and AI analysis. The number of AI-consistent and AI-inconsistent PWMs (one PWM per RBP) discovered by each program using different significance thresholds is shown. For each RBP, the top PWM discovered by each method was used for comparison.
(E) Among the AI-consistent PWMs discovered by each program at p<0.05, the number of RBPs showing low (D≤0.05) or high (D>0.05) D-scores is shown.