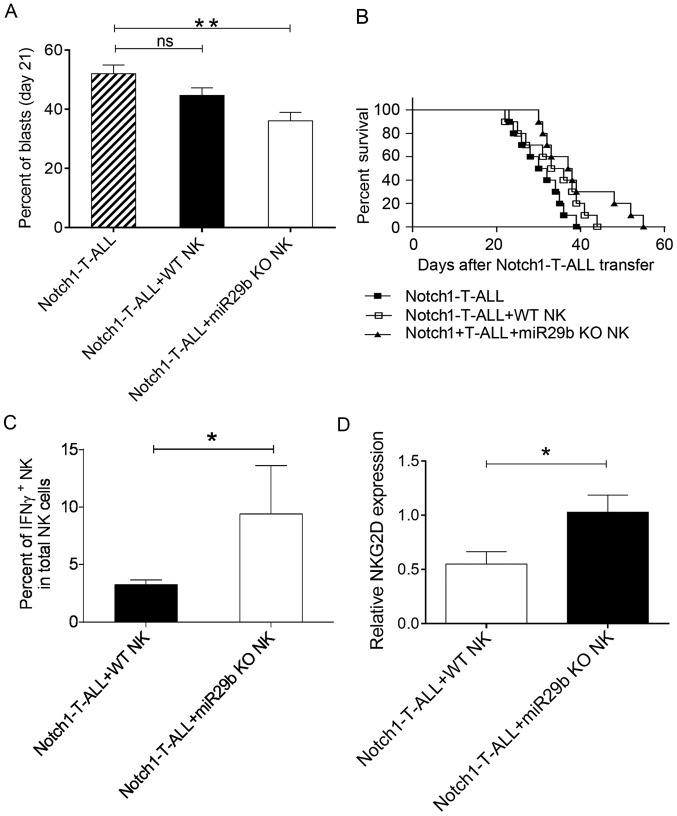
Figure 4.
miR29b KO NK cells decrease ALL progression. Three groups of C57BL/6 Rag2−/− mice received either 2×105 Notch1-T-ALL blasts without NK cells; 2×105 Notch1-T-ALL blasts and 2×107 WT NK cells from WT C57BL/6 mice; or 2×105 Notch1-T-ALL blasts and 2×107 miR-29b KO cells from C57BL/6 miR29ab1−/−mice. (A) Percentages of circulating Notch1-T-ALL blasts were evaluated using flow cytometry. (B) Survival rate was compared between three groups. Notch1-T-ALL, ■; Notch1-T-ALL+WT NK cells, □; and Notch1-T-ALL+miR-29b KO NK cells, ▲. (C) Percentage of IFNγ+ NK cells in the NK1.1+CD3−NK cell population from Notch1-T-ALL mice transfused with WT NK cells or miR-29b KO NK cells. (D) Relative NKG2D expression levels in NK cells from Notch1-T-ALL mice transfused with WT NK cells or miR-29b KO NK cells. A: n=10 mice per group; B: n=10 per group (Kaplan-Meier curve and log-rank test); C and D: n=10 mice per group. The data are presented as the mean ± SD. *P<0.05 and **P<0.01, as determined using one-way ANOVA or the unpaired Student's t-test. miR, microRNA; KO, knock-out; T-ALL, T-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia; NK, natural killer; WT, wild type; Notch1, neurogenic locus notch homolog protein 1; IFN, interferon; NKG2D, natural killer receptor group 2, member D; ns, not significant.