Figure 6.
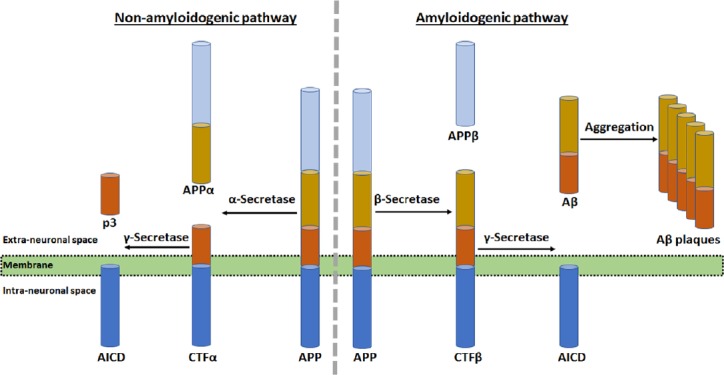
Amyloid precursor protein (APP) proteolysis in two different pathways and role of amyloid-beta (Aβ) plaques in neurodegeneration in the AD brain.
The non-amyloidogenic (normal) pathway of APP proteolysis produces an N-terminal fragment (called APPα) and a membrane-bound C-terminal fragment α (CTFα). In the membrane, CTFα is then cleaved to yield a soluble N-terminal fragment (p3) and a membrane-bound C-terminal fragment called APP intracellular domain (AICD). The amyloidogenic (abnormal) pathway of APP proteolysis produces N-terminal fragment (called APPβ) and membrane-bound C-terminal fragment β (CTFβ). Then, CTFβ is cleaved to generate a soluble N-terminal fragment (Aβ) and membrane-bound C-terminal fragment (AICD) as before. Accumulation of Aβ in the extracellular space causes its aggregation to form Aβ plaques in the brain.
