Figure 1.
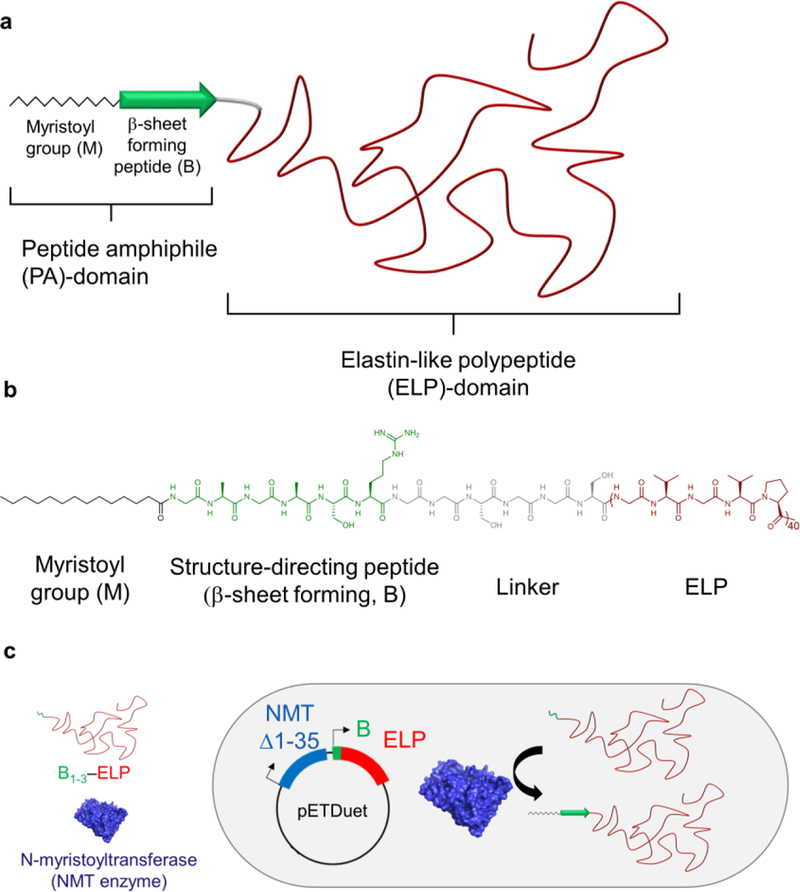
Schematic of the structure and synthesis of FAMEs through post-translational modification of ELPs. a) FAMEs consist of three main components: a myristoyl group (zigzag chain) and a structure-directing peptide sequence (green arrow, B) — which together form a PA domain — and an ELP domain (shown in red). b) Molecular structure of M-B1-ELP shown as an example. In addition to the three main components, a short, flexible linker is also incorporated into the FAMEs, to ensure that myristoylation of the B domain is not sterically hindered by ELP (see text). c) Schematic representation of the one-pot expression and post-translational lipidation by tandem expression of the NMT enzyme (Δ1–35) and B1–3–ELP using pETDuet expression vector in which B is a peptide that is designed de novo to be recognized by the NMT enzyme as a substrate, and myristoylated.
