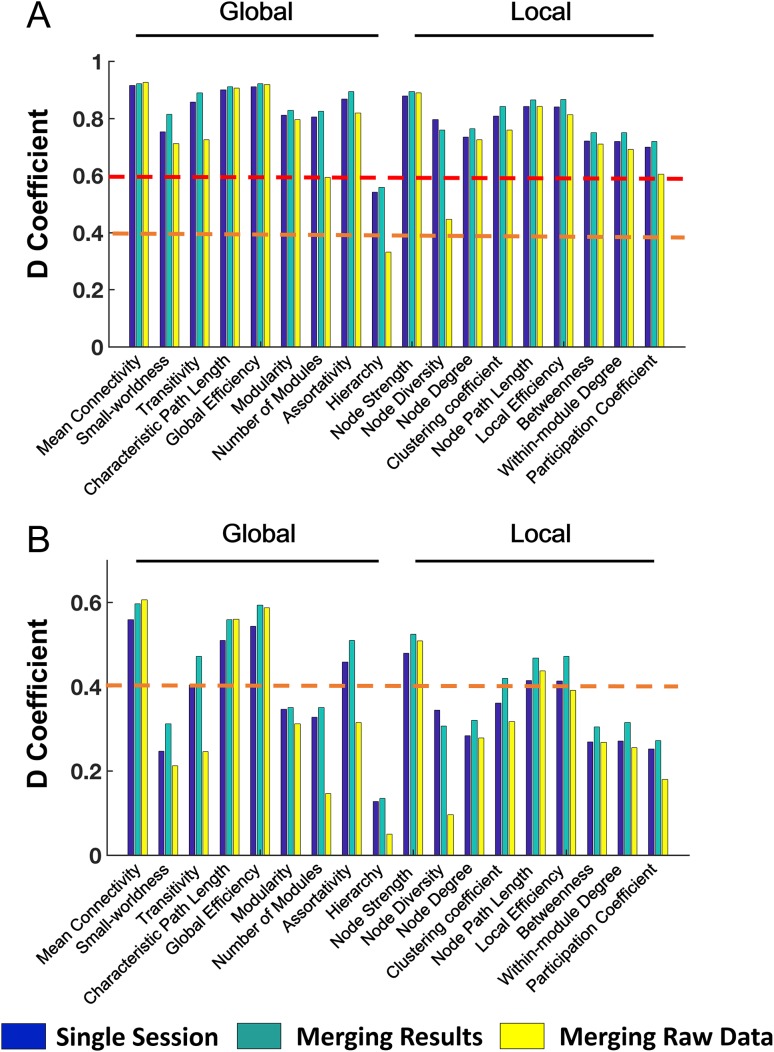
Figure 6.
Reliability comparison of 2 data aggregation approaches (A: G study; B: D study). The “merging results” approach (i.e., averaging properties across sessions) was associated with significantly higher reliability compared with those from single session, while the “merging raw data” approach (i.e., concatenation of time series from both sessions) had significantly reduced reliability. The orange dashed lines indicate the level of fair reliability (⩾0.4) and the red dashed lines indicate the level of good reliability (⩾0.6).