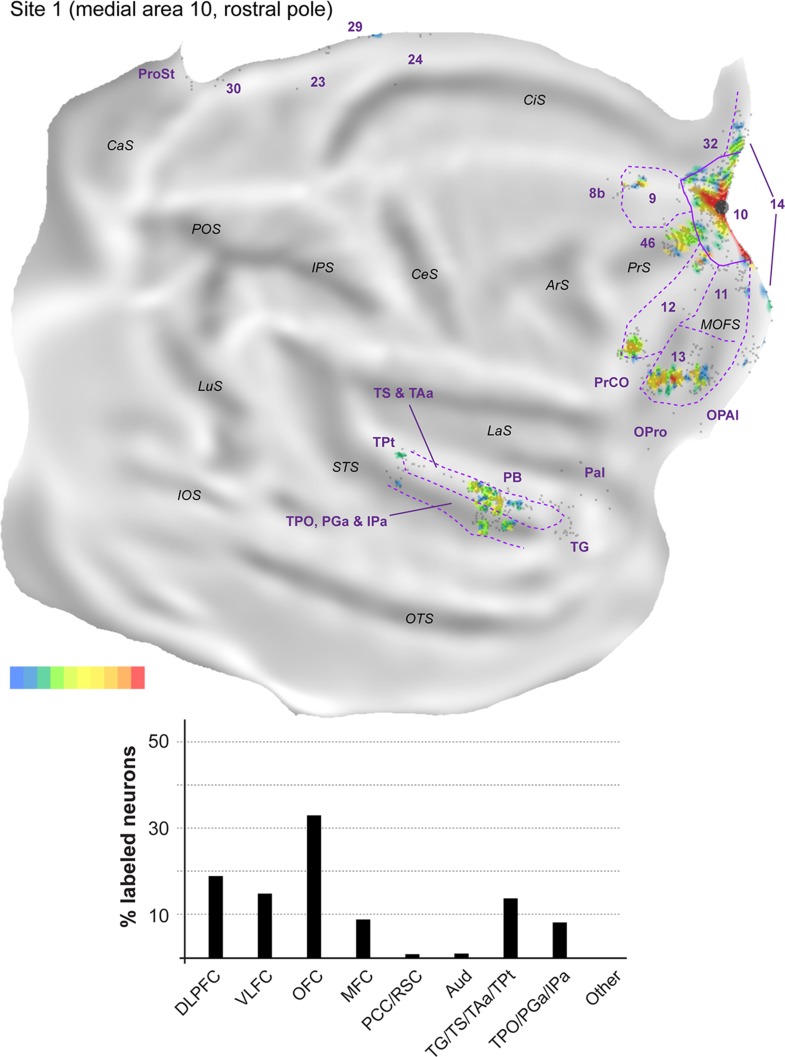
Figure 4.
Top: 2D “unfolded” reconstruction of the cerebral cortex in animal FR01, showing the pattern of label resulting from an injection of FR in area 10 (site 1). Large aggregations of labeled neurons are indicated by color, as a percentage of the maximum density observed (bottom right scale; red = 91–100% of the maximum density across all layers, blue ≤10% of the maximum density). Gray points represent individual neurons. Black circles indicate the centers of the injection sites. ArS, arcuate sulcus; CaS, calcarine sulcus; CeS, central sulcus; CiS, cingulate sulcus; IOS, inferior occipital sulcus; IPS, intraparietal sulcus; LaS, lateral sulcus; LuS, lunate sulcus; MOFS, medial orbital frontal sulcus; OTS, occipito-temporal sulcus; POS, parieto-occipital sulcus; PrS, principal sulcus; STS, superior temporal sulcus. Bottom: Summary of the percentages of extrinsic projection neurons labeled in different parts of the cerebral cortex (see Table 2 for details). DLPFC, dorsolateral prefrontal cortex (areas 8b, 9, 46); VLFC, ventrolateral frontal cortex (subdivisions of area 12, and precentral opercular cortex, PrCO); OFC, orbitofrontal cortex (areas 11, 13, OPal, and OPro [orbital proisocortex]); MFC, medial frontal cortex (areas 14, 24, 25, and 32); PCC/RSC, posterior cingulate cortex and retrosplenial cortex (areas 23, 29, 30, and prostriata); Aud, auditory cortex (rostrotemporal [RT] core, lateral and MB, and parabelt areas); TG/TS/TAa/TPt, subdivisions of the superior temporal auditory association cortex; TPO/PGa/IPa, subdivisions of the superior temporal polysensory cortex.