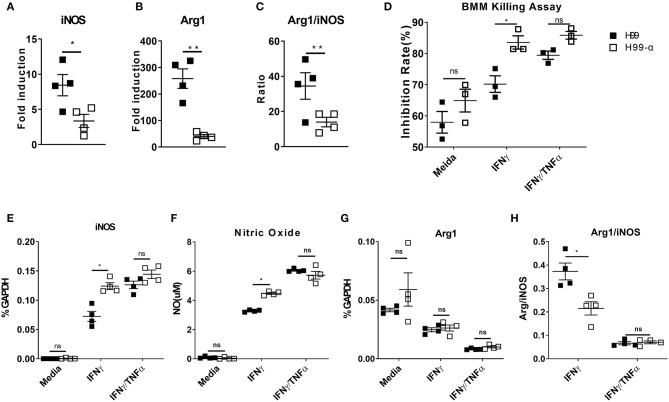
Figure 8.
Expression of the murine TNF-α diminishes alternative activation of lung macrophages and promotes the anti-cryptococcal activity of BMMs in vitro. (A,B) mRNA expression of iNOS and Arginase (Arg1) from adherence-enriched macrophages at 14 dpi were determined by RT-qPCR. (C) Arg1/iNOS ratio was calculated as a readout of M2 vs. M1 activation bias. BMMs were co-cultured with mouse serum (10%) opsonized H99α or H99 in the medium only, IFN-γ, or IFN-γ together with TNF-α. Inhibition rates of fungal growth (D), iNOS mRNA expression by BMM (E), NO production in the supernatant (F), Arg1 mRNA expression (G), and Arg1/iNOS ratio (H) were evaluated. Notably, significantly higher growth inhibition rate, iNOS expression and NO production were found in macrophages challenged with H99-α than H99 in the presence of IFN-γ. Results represent mean ± SEM, N = 4 for each group (*P < 0.05; **P < 0.01; ns, no significant difference).