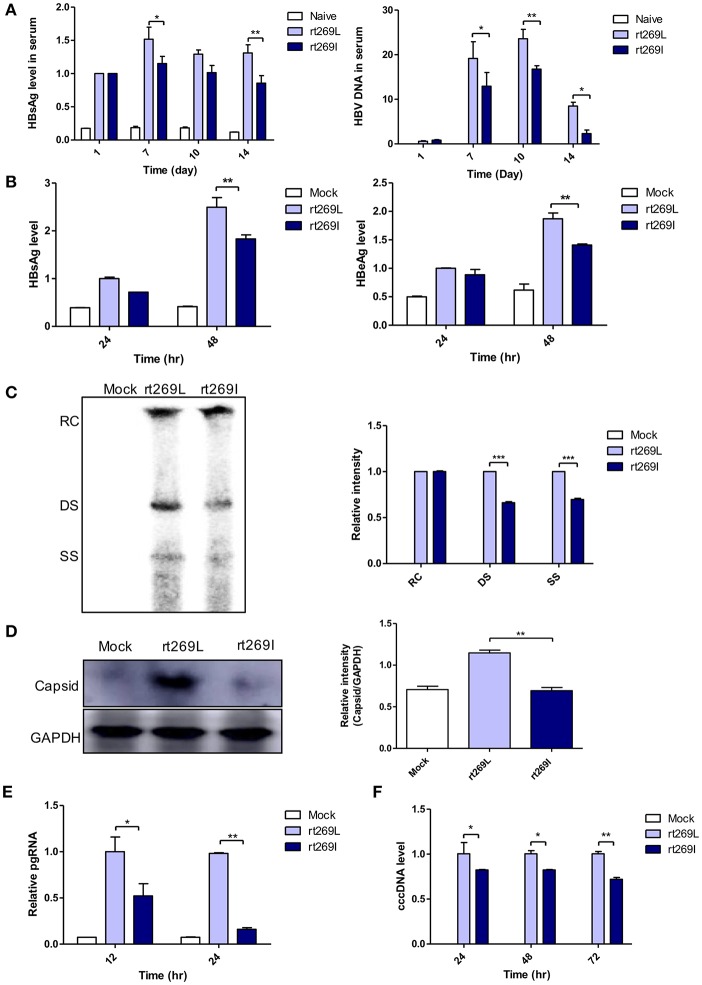
Figure 1.
rt269I vs. rt269L led to reduced viral replication in in vivo and in vitro analyses. (A) Both HBV-encoding DNA and pSV-β-Galactosidase was injected by hydrodynamic tail vein injection into C57BL/6 mice. HBsAg and HBV DNA in serum were determined by HBsAg ELISA and normalized with β-Galactosidase (n = 5). (B–E) Plasmid DNA was transfected into HepG2 cells and the replicative capacities were analyzed. (B) The level of secreted HBsAg and HBeAg were detected using ELISA. (C) HBV DNA was compared via Southern blotting at 48 h post-transfection. (D) Western blot analyses of intracellular capsid forms were performed by using anti-HBcAg antibody on naïve gel at 24 h after transfection. (E) The translation mediates pgRNAs were detected by qRT-PCR. (F) Linear DNA removed from CMV promoter was transiently transfected into HepG2 cells. The intermediates of transcripts cccDNA were determined using qPCR. Data were normalized to β-Galactosidase enzyme assay. One- and two-way ANOVA were used. *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001.