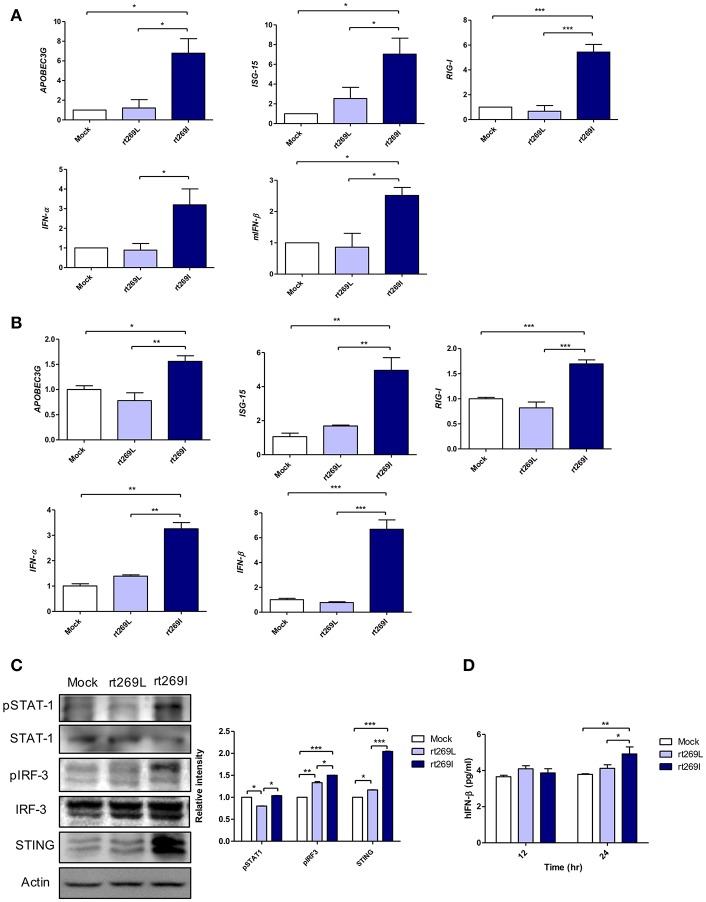
Figure 2.
rt269I enhanced IFN-I production in HepG2 cells. (A) Both HBV-encoding DNA and pSV-β-Galactosidase were injected by hydrodynamic tail vein injection into C57BL/6 mice (n = 5). The transcription level of APOBEC3G, ISG-15, RIG-I, IFN-α, and IFN-β were determined by qRT-PCR from mice hepatocytes on 4 days post-infection, and normalized with 18S rRNA and β-Galactosidase. (B–D). HepG2 cells were transfected with HBV DNA and the expression levels of IFN-I-related genes were assessed. (B) The mRNA level of IFN-I-related genes was determined using qRT-PCR at 12 h after transfection, and data were normalized to 18S rRNA. (C) The upstream proteins of the IFN-I signaling pathway were detected via Western blotting at 48 h post-transfection. (D) The secreted IFN-β was measured with ELISA at 24 h post-transfection. Data were and normalized to β-Galactosidase assay. One- and two-way ANOVA were used. *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001.