Table 2.
Optimization of amines for palladium/enamine catalysisa
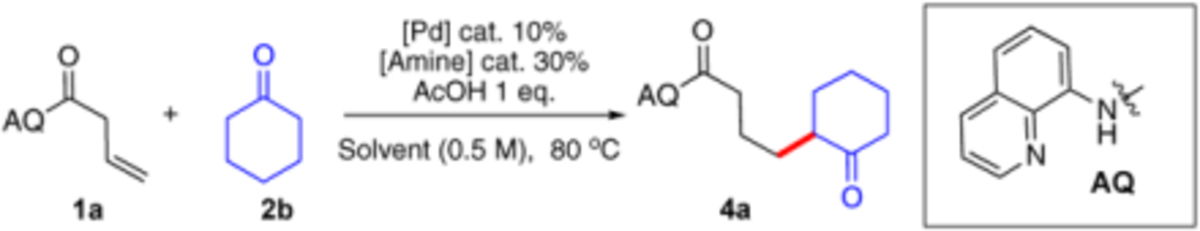 | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Entry | [Pd] | [Amine] | Sol. | Conv.b | Yieldb | ee%c |
| 1d | Pd(OAc)2 | n/a | MeCN | <5% | <5% | - |
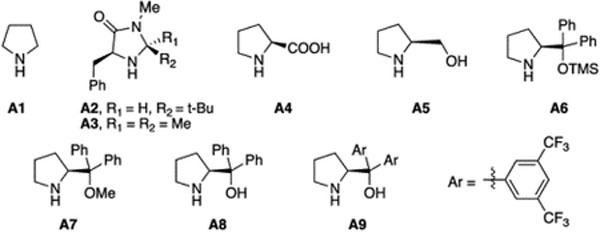
| 2 | Pd(OAc)2 | A1 | Tol | 100% | 95% | - |
| 3 | Pd(OAc)2 | A2 or A3 | Tol | <20% | <20% | 0 |
| 4 | Pd(OAc)2 | A4 | Tol | 62% | 54% | 11% |
| 5 | Pd(CH3CN)2Cl2 | A4 | Tol | 79% | 77% | 15% |
| 6 | Pd(CH3CN)2Cl2 | A5 | Tol | 100% | 90% | 33% |
| 7 | Pd(CH3CN)2Cl2 | A6 | Tol | 100% | 91% | 63% |
| 8 | Pd(CH3CN)2Cl2 | A7 | Tol | 100% | 57% | <5% |
| 9 | Pd(CH3CN)2Cl2 | A8 | Tol | 100% | 96% | 65% |
| 10 | Pd(CH3CN)2Cl2 | A9 | Tol | 100% | 97% | 71% |
| 11e | Pd(CH3CN)2Cl2 | A9 | Tol | 100% | 97% | <5% |
| 12f | Pd(CH3CN)2Cl2 | A9 | Tol | 60% | 55% | 93% |
| 13f | Pd(CH3CN)2Cl2 | A9 | neat | 100% | 99% (95%)g | 88% |
 | ||||||
Reaction conditions: [Pd] cat. (10 mol%), [amine] cat. (30 mol%), AcOH (1 eq.), solvent (0.5 M), under 80 °C, 24 hours.
Conversion and yield were determined by 1H NMR using 1,3,5-trimethoxybenzene as internal standard.
ee value was determined by HPLC.
120 °C, 36 hours.
72 h.
60 °C, 24 hours.
Isolated yield.
