Figure 3.
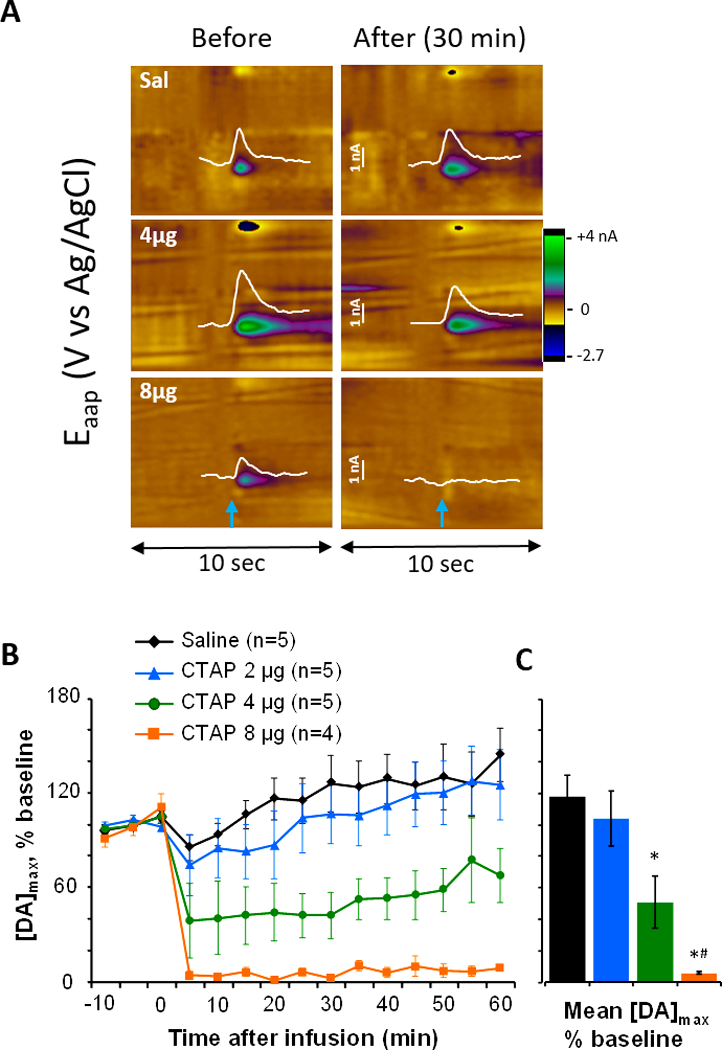
Infusion of CTAP to the nucleus accumbens core dose-dependently reduces evoked dopamine release. The selective MOR antagonist CTAP (2, 4, and 8 μg) or saline was infused to the area of dopamine measurement via an infusion cannula approximately 150 μm from the voltammetric electrode. (A) Current-versus-time traces at the oxidation potential of dopamine (white, 7 seconds) are overlaid on color plots of evoked dopamine release from individual rats before and after saline, 4 μg and 8 μg CTAP infusion. The time of electrical stimulation is indicated by blue arrows. Infusion of 4 μg CTAP partially blunted electrically-evoked dopamine release while 8 μg CTAP blocked it. (B) and (C): Composite data show the dose-dependent effects of CTAP on evoked dopamine release over time (B) and averaged across post-infusion time points (C). Electrically-evoked dopamine was unchanged by saline and 2 μg CTAP, but reduced by 4 and 8 μg CTAP. Statistics were calculated on the data in panel C: * different from Saline, p<0.05; # different from 2 μg CTAP, p<0.05.
