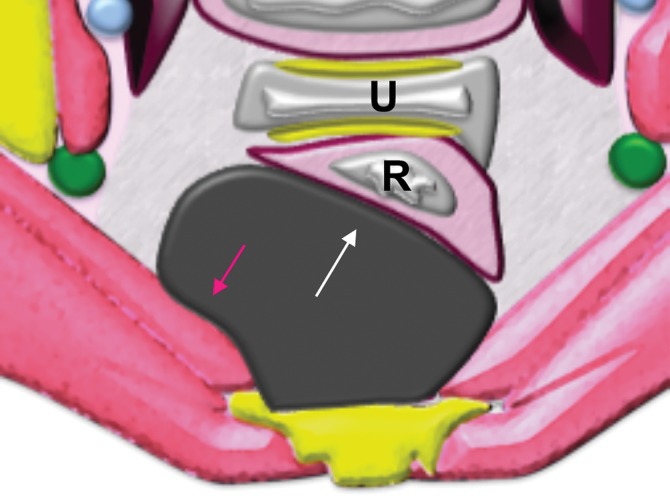
Figure 4c.
Extraperitoneal pelvic masses. R =rectum, U = uterus. (a) Axial T2-weighted image shows a multicystic retrorectal lesion that displaces the rectum anteriorly (white arrow) and effaces the right iliococcygeal muscle (pink arrow), consistent with an extraperitoneal mass (tailgut cyst). (b) Axial contrast-enhanced MR image shows a chordoma in the retrorectal space, causing anterior and central displacement of the uterus (white arrow) and anterior displacement of the left internal iliac vessels (pink arrow). (c, d) Imaging features of pelvic masses that arise in the extraperitoneal space. (c) Drawing shows anterior and central displacement of the rectum by an extraperitoneal mass (white arrow) with mass effect on the pelvic muscles (pink arrow). (d) Drawing shows central displacement of the uterus (white arrow) and anterior displacement of the right iliac vessels (pink arrow).