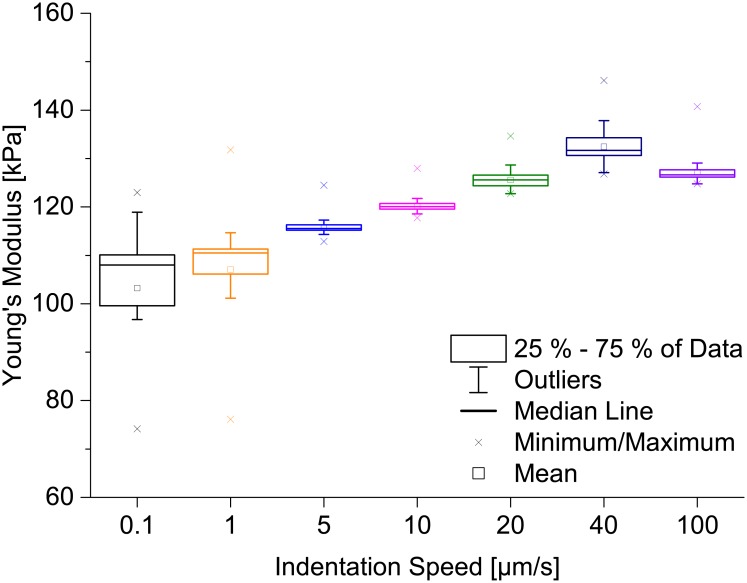
Fig 4. Dependence of Young’s moduli on indentation speed for a thin PAAm sample.
For each of several indentation speeds ranging from 0.1 μm/s to 100 μm/s, 250 force-distance curves (10 curves at each of 25 positions) or 150 force-distance curves (10 curves at each of 15 positions) for 0.1 μm/s were measured and the distributions of Young’s moduli are presented as boxplots. The AFM measurements result in higher Young’s moduli for higher indentation speeds, except for 100 μm/s. The dependence of the Young’s modulus on the indentation speed is probably due to PAAm being viscoelastic [45]. Viscoelastic properties can be neglected on longer timescales [3] (i.e. for quasi-static indentation speeds such as 0.1 μm/s).