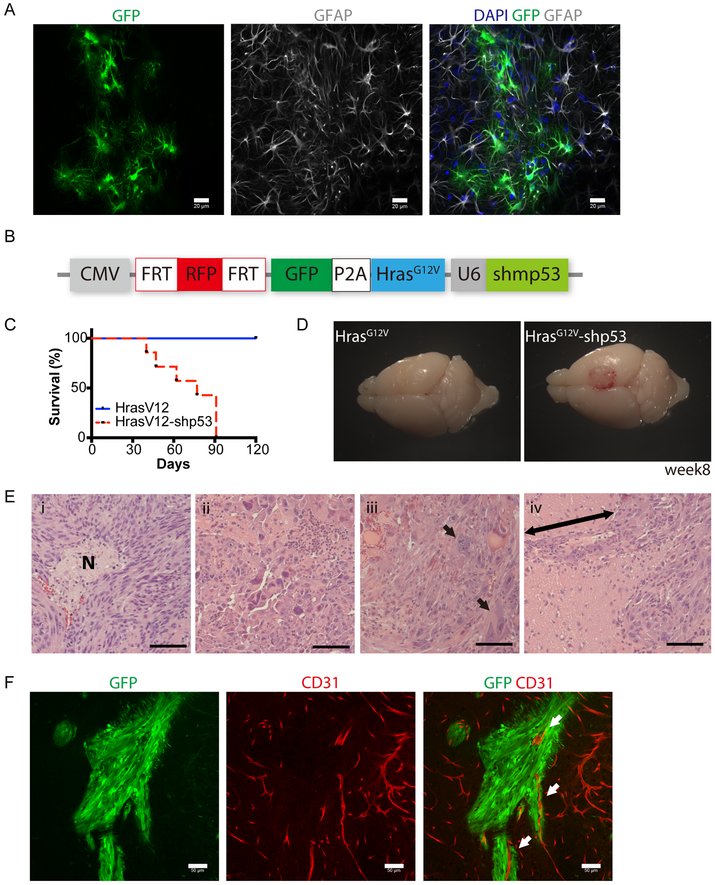
Fig. 3. Cell-type specific delivery of oncogenes to model gliomas in GFAP-FLPo.
(A) Immunostaining analysis of GFAP (gray) and GFP (green) expression in the cortex of GFAP-FLPo animals stereotaxically injected with lentiviral vectors harboring CAG-FRT-STOP-FRT-GFP into the cortex. Scale bars, 20 μm. More than 5 animals were subjected to the analysis. Similar results were obtained in two independent experiments.
(B) A diagram of the FLP/ FRT-based lentiviral vector to induce tumorigenesis in GFAP-FLPo animals. CMV: cytomegalovirus immediate-early promoter. P2A: porcine teschovirus-1 derived 2A self-cleaving peptide sequence. U6: RNA polymerase III-based promoter from mouse U6 small nuclear RNA. shp53: shRNA against mouse Trp53.
(C) Survival analysis of GFAP-FLPo mice after stereotaxic injection with either CMV-FRT-RFP-FRT-GFP-P2A-HrasG12V-U6-shp53 or CMV-FRT-RFP-FRT-GFP-P2A-HrasG12V. Similar results were obtained in at least three independent experiments.
(D) Representative images of the brains from GFAP-FLPo animals injected with either CMV-FRT-RFP-FRT-GFP-P2A-HrasG12V-U6-shp53 or CMV-FRT-RFP-FRT-GFP-P2A-HrasG12V into the cortex.
(E) H&E staining analysis of tumors established in the brain of GFAP-FLP mice after stereotaxic injection with CMV-FRT-RFP-FRT-GFP-P2A-HrasG12V-U6-shp53. (i) Necrotic area with the spindle-shaped cells, (ii) pleomorphism, (iii) multinucleated gigantic cells, (iv) perivascular invasion. Arrow marks perivascular infiltration of cells. Scale bars, 50 μm. Similar histological results were observed in sections from more than six animals.
(F) Immunostaining analysis of CD31 (red) and GFP (green) expression in the brain from GFAP-FLPo mice after stereotaxic injection CMV-FRT-RFP-FRT-GFP-P2A-HrasG12V-U6-shp53. Arrows mark CD31-positive blood vessel surrounded by GFP-positive glioma cells. Scale bars, 20 μm.