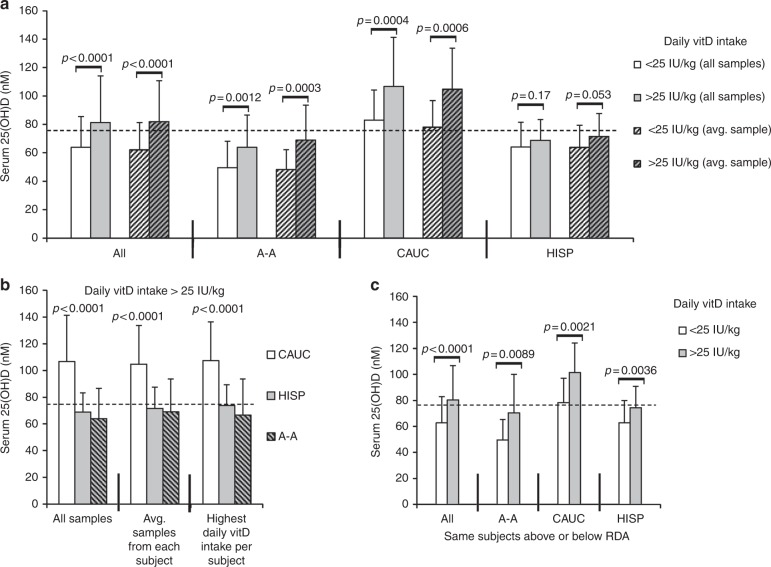
Fig. 1.
Effects of vitD intake on serum 25-D concentrations in children (all VDBP isoforms). a Mean 25-D (nmol/L) compared between Caucasian, Hispanic, and African-American children regularly reaching the vitD RDA (normalized as >25 IU/kg; representing 400–600 IU daily intake), or below the RDA at the time of annual serum collection. Statistics calculated using all available serum samples or the average of 25-D values for each subject’s samples. b Direct comparisons of serum 25-D in different groups of children meeting or exceeding vitD RDA; all samples, average of each subject’s samples, or single sample from each subject at the time of highest daily vitD intake (80 total subjects). c Comparisons of mean 25-D within the same children who were both below and above the vitD RDA at different annual serum collections (55 total subjects). P values <0.05 considered significant. Dashed line in each graph represents threshold serum concentration of ≥75 nmol/L 25-D. vitD, Vitamin D, VDBP, vitamin D binding protein; 25-D, 25-hydroxyvitamin D, RDA recommended daily allowance