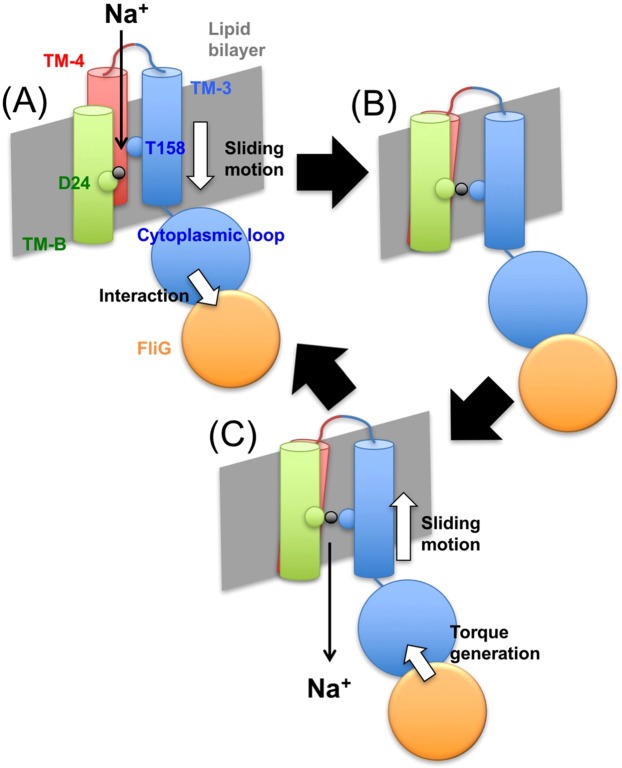
Figure 8.
A mechanochemical model for the flagellar motor. Interaction of the cytoplasmic loop in PomA with FliG induces sliding motions of TM-3 and TM-4 toward cytoplasmic side (A). This rearrangement approaches T158 in TM-3 toward D24 in TM-B and forms Na+ binding site by three modes of interaction (B). After release of the Na+ into the cytoplasmic side, TM-3 and TM-4 return to the original position. This re-sliding motion induces a conformational change in the cytoplasmic loop to produce torque at the interface with FliG (C).