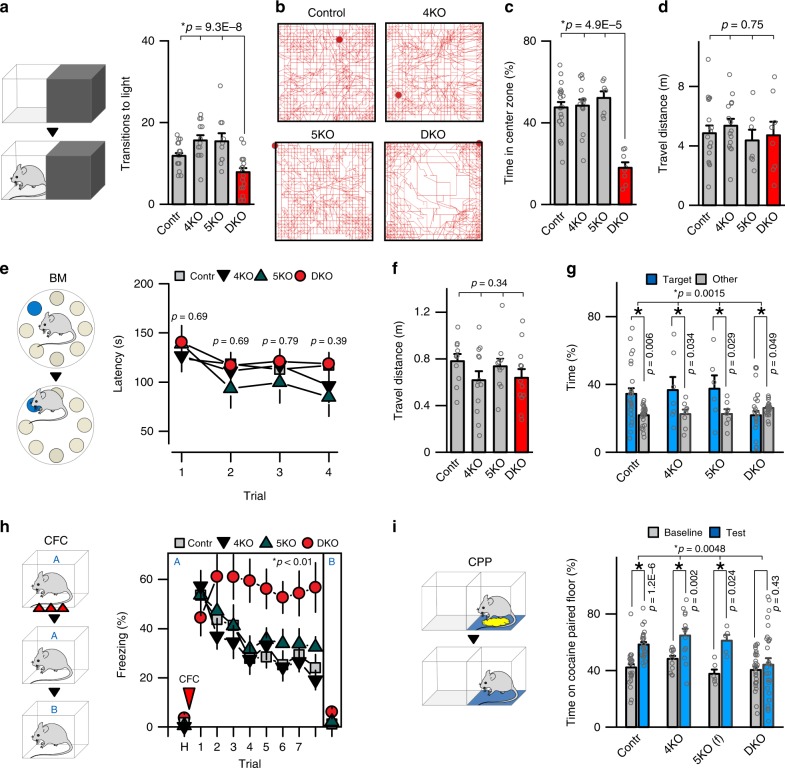
Fig. 3.
Behavior of class IIa HDAC-deficient mice. Animals of indicated genotypes were examined at p60. See also Supplementary Fig. 7 and Methods. a Analysis of anxiety-like behavior in the dark–light transfer test. Schematics of experimental setup and averaged transitions to light are shown. Control: n = 19 mice; 4KO: n = 13; 5KO: n = 10; DKO: n = 19. b–d Locomotor activity in the open field setup. b Typical tracks during 30 min sessions. c Averaged times spent in the center zone. d Total travel distances. Control: n = 20; 4KO: n = 15; 5KO: n = 7; DKO: n = 8. e–g Assessment of spatial memory in the Barnes maze. e Schematics of the maze and averaged latencies to escape through the tunnel in each of the four sequential daily training sessions. Control: n = 30; 4KO: n = 13; 5KO: n = 10; DKO: n = 30. f Total travel distances in the maze during training. g Memory retrieval in the probe test with escape tunnel removed. Graph shows averaged percentages of time spent in the correct (target) and other quadrants of the maze. Control: n = 30; 4KO: n = 12; 5KO: n = 11; DKO: n = 29. h Acquisition and extinction of associative fear memory. Mice were allowed to habituate (H) and then subjected to CFC in Context A. Freezing was measured on a daily basis in the same or irrelevant context (Context B). Control: n = 15; 4KO: n = 14; 5KO: n = 11; DKO: n = 11. i Conditional place preference (CPP) test. Graph shows averaged times spent on cocaine-paired floor. Control: n = 27; 4KO: n = 13; 5KO: n = 6§; DKO: n = 29. All quantifications are represented as Mean ± SEM. *p < 0.05 (defined by t-test and ANOVA). Actual p-values are indicated in each graph (vertical for t-test and horizontal for ANOVA). § No sex-related differences in behavior were observed with exception of HDAC5-deficient mice in the CPP test, where only females had preference for cocaine-paired floor