Fig. 3.
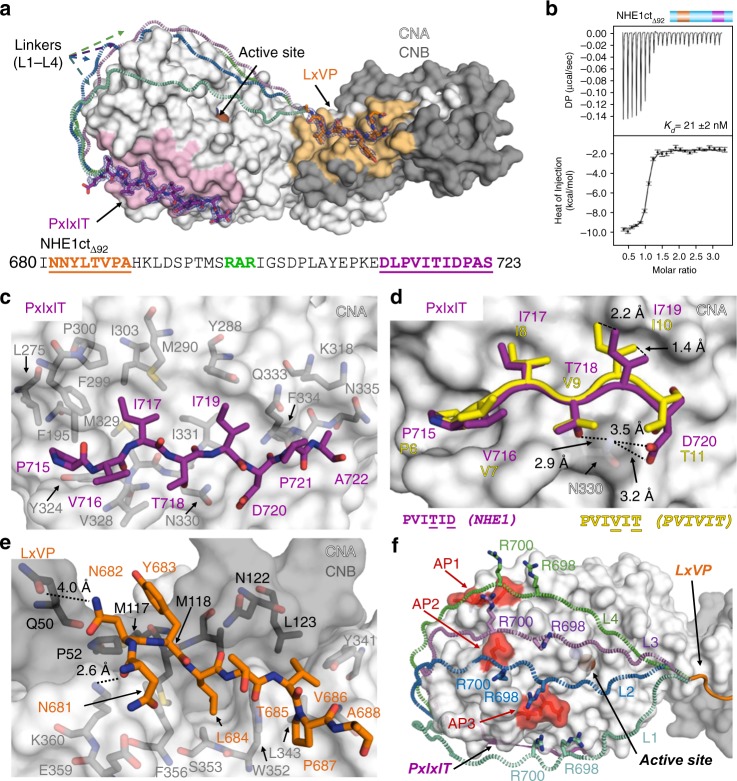
The NHE1 CN-binding motifs are connected by a dynamic linker. a Crystal structure of NHE1ctΔ92:CN. NHE1 residues are shown as sticks in dark orange (NHE1 N681-A688, LxVP motif) or magenta (NHE1 D713-S723, PxIxIT motif); the 2Fo–Fc electron density map is contoured at 1σ (blue mesh). CN is shown as surface (CNA: white, CNB: gray, the LxVP and PxIxIT-binding pockets are shaded light orange and light pink, respectively). Bound metals are shown as spheres (Fe: brown, Zn: slate). Multiple modeled conformations of the linker are illustrated with dashed lines (L1–L4) reflecting the dynamic nature of the linker. NHE1ctΔ92 sequence; residues modeled into electron density are underlined, with the LxVP and PxIxIT sequences colored as in a; 698RAR700 highlighted in green. b ITC data for NHE1ctΔ92:CN binding (n = 2). c NHE1 PxIxIT (715PVITIDPA722; magenta) interactions with CNA (white). NHE1 P715, I717, and I719 bind in three deep hydrophobic pockets of CNA. d Overlay of NHE1 residues 715PVITID720 with that of the 6PVIVIT11 peptide structure (yellow, PDBID, 2P6B [http://dx.doi.org/10.2210/pdb2P6B/pdb]; CNA from both structures was superimposed). NHE1 I719 rotates out of the pocket compared to the bound 6PVIVIT11 peptide. CNA N330 is shown as sticks. NHE1 residues T718 and D720 form hydrogen bonds with CNA N330. e NHE1 LxVP (681NNYLTVP687; dark orange) interactions at the CNA/CNB (white/gray) interface. NHE1 N681 and N682 form hydrogen bonds with CNA K360 and CNB Q50, respectively. f Multiple modeled conformations of the linker bound to CN. Linkers shown in mint (L1), blue (L2), light purple (L3), and green (L4) dashed loops. NHE1 R698 and R700 side chains are shown as sticks while CNA is shown as surface. Acidic patches (AP1:E205/D211/D229; AP2: E246; AP3: E237/D238) are highlighted in red