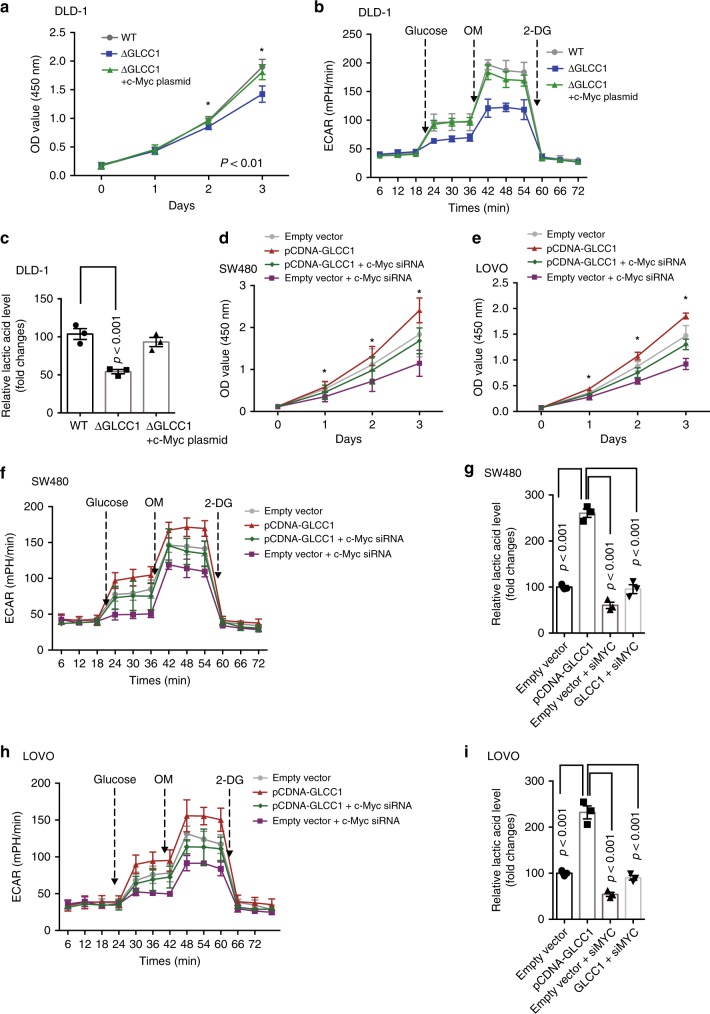
Fig. 5.
C-Myc participate in the biological function of GLCC1 in CRC cells. a Cell proliferation assay was performed in DLD-1-wt, DLD-1ΔGLCC1 cells transfected with control or c-Myc overexpression plasmid; n = 6. b The change of ECAR level was detected in DLD-1-wt, DLD-1ΔGLCC1 cells transfected with control or c-Myc overexpression plasmid; n = 3. c The relative lactic acid level was measured in DLD-1-wt, DLD-1ΔGLCC1 cells transfected with control or c-Myc overexpression plasmid; n = 3. d, e Cell proliferation assay was performed in SW480 (d) and LoVo (e) cells cotransfected with control and c-Myc siRNA or cotransfected with GLCC1 overexpression plasmid and c-Myc siRNA; n = 6. f The change of ECAR level was detected in SW480 cells cotransfected with control and MYC siRNA or cotransfected with GLCC1 overexpression plasmid and c-Myc siRNA; n = 3. g The relative lactic acid level was measured in SW480 cells cotransfected with control and c-Myc siRNA or cotransfected with GLCC1 overexpression plasmid and c-Myc siRNA; n = 3. h The change of ECAR level was detected in LoVo cells cotransfected with control and c-Myc siRNA or cotransfected with GLCC1 overexpression plasmid and c-Myc siRNA; n = 3. i The relative lactic acid level was measured in LoVo cells cotransfected with control and c-Myc siRNA or cotransfected with GLCC1 overexpression plasmid and c-Myc siRNA; n = 3. Data are presented as the mean ± SE. p-values were calculated by one-way ANOVA followed by SNK multiple comparison test. *p < 0.05