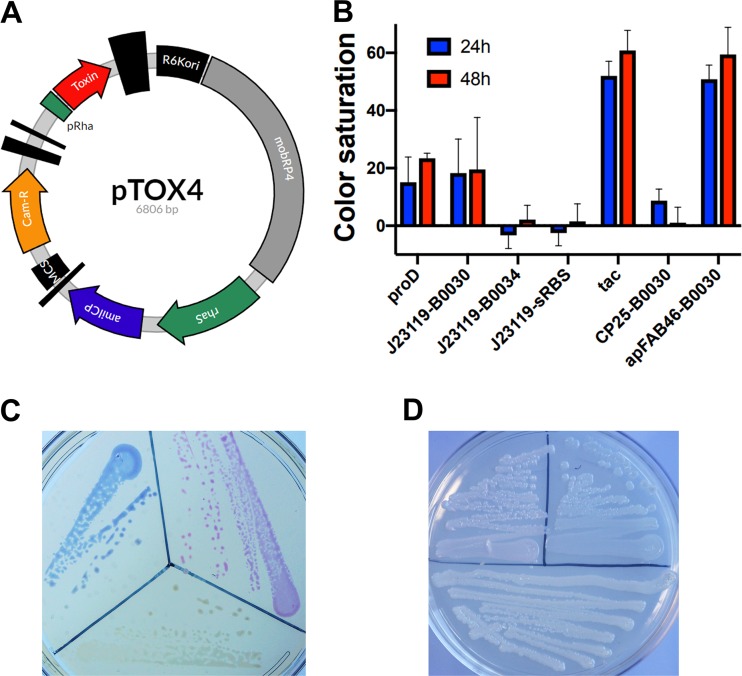
FIG 4.
A chromoprotein module facilitates monitoring of conjugation. (A) Plasmid map of pTOX4. R6Kori, the R6K origin of replication; mobRP4, the mobilization region from the RP4 conjugative plasmid; rhaS encodes the rhamnose transcriptional activator; amilCP, AmilCP gene, encoding the blue AmilCP chromoprotein; MCS, multiple-cloning site; Cam-R, chloramphenicol resistance cassette; pRha, rhamnose promoter. The vertical black bars of various widths represent terminators. (B) The tac promoter and apFAB46-B0030 allow optimal AmilCP gene expression. Shown is the relative color saturation at 24 h and 48 h of pTOX4-containing colonies with various promoters and ribosome-binding sites (RBS) (described in more detail in Materials and Methods). (C) Depiction of donor E. coli containing (clockwise from bottom) pTOX without chromoprotein, with the tac-AmilCP gene, and with the apFAB46-B0030-TsPurple gene after 24 h at 37°C. (D) E. cloacae pTOX merodiploids (clockwise from bottom) without chromoprotein, with the tac-AmilCP gene, and with the apFAB46-B0030-TsPurple gene after 24 h at 37°C and an additional 24 h at 25°C.