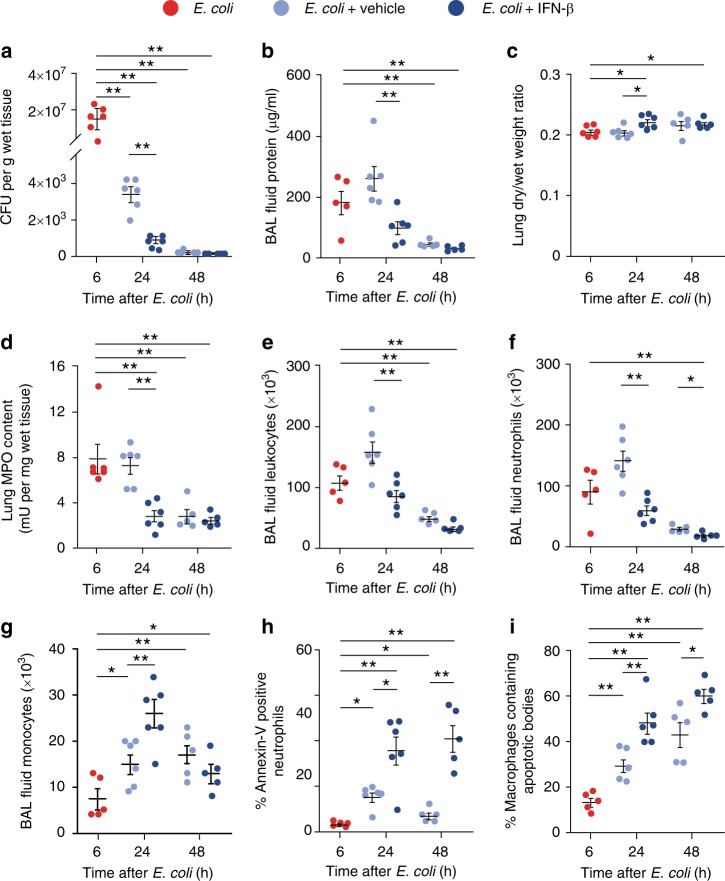
Fig. 8.
IFN-β treatment accelerates the resolution of E. coli pneumonia. Female C57BL/6 mice were injected intratracheally with 5*106 live E. coli. Six hours later (at the peak of inflammation), they were treated with mouse recombinant IFN-β (50 ng/20 g b.w., intraperitoneally) or vehicle. At 24 or 48 h post-E. coli instillation, lungs were removed without lavage and analyzed for E. coli content (a), lung dry-to-wet weight ratio (c) and tissue MPO activity (d). In separate groups of mice bronchoalveolar lavage fluid protein concentration (b), total leukocyte (e), neutrophil (f) and monocyte/macrophage numbers (g), the percentage of annexin-V-positive (apoptotic) PMN (h), and the percentage of macrophages containing apoptotic bodies (i) were determined. Results are means ± SEM (n = 6 mice per group for 6 and 24 h and 5 mice per group for 48 h). *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01 (Dunn’s multiple contrast hypothesis test). Source data are provided as a Source Data file