Figure 2.
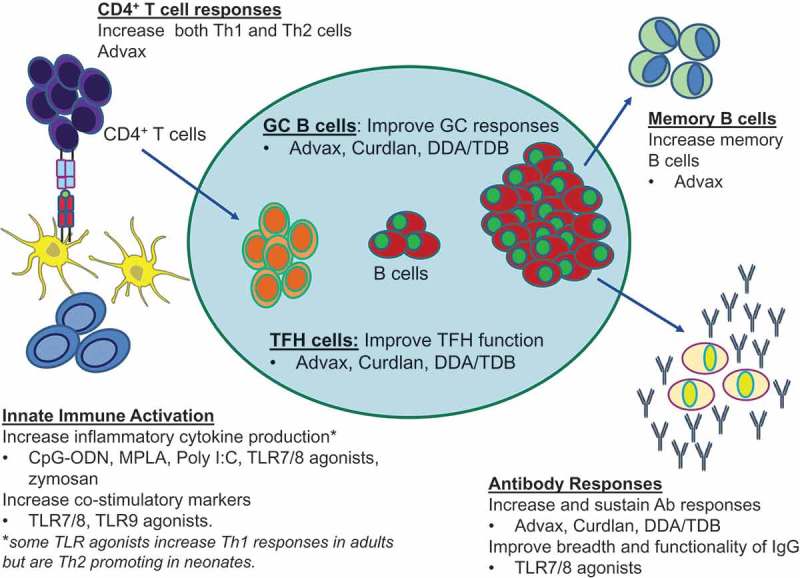
Overcoming functional differences in neonatal immune system through use of vaccine adjuvants. Adjuvants enhance immunogenicity of neonatal vaccines through innate activation and via enhancement of multiple aspects of adaptive immunity. Adjuvants can activate APC, such as monocytes and dendritic cells and increase cytokine production and co-stimulatory marker expression, which improve the priming of naïve CD4+ T cells. Following activation and antigen presentation, CD4+ T cells can differentiate into T follicular helper cells, which are necessary in the germinal center reaction to assist B cells in generating effective antibodies. Improvement in memory and plasma B cells enhances antigen detection and neutralization through increased production of high-affinity antibodies. Abbreviations/key to understanding: TLR = Toll-like receptor; CpG-ODN = CpG-oligodeoxynucleotides; MPLA = Monophosphoryl lipid A; DDA/TDB = dimethyldioctadecyl ammonium (DDA) and trehalose 6,6′-dibehenate (TDB); 3M-052-SE = a TLR7/8 agonist containing imidazoquinoline/Oil-in-water squalene emulsion (SE); Advax = delta inulin adjuvant.
