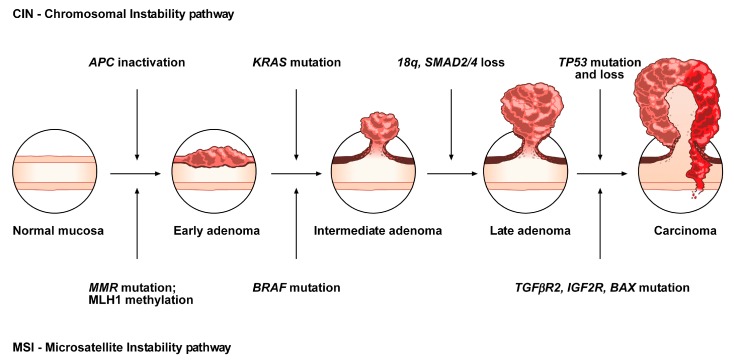
Figure 1.
Conventional adenoma-to-carcinoma sequence. The chromosomal instability (CIN) pathway begins with bi-allelic mutations in the tumor suppressor gene APC within the normal colonic mucosa. The latter progressively differentiate into adenocarcinoma upon acquisition of additional mutations in the genes KRAS, SMAD4, and TP53, with consequent dysregulation of the Wnt/β-catenin, MAPK, PI3K and TGF-β signaling pathways. Alternatively, the MSI pathway involves an initial alteration of the Wnt signaling that leads to the formation of an early adenoma. Then, BRAF mutation followed by alterations of the genes TGFBR2, IGF2R, and BAX, participate in the progression toward the intermediate and late stages of carcinogenesis.