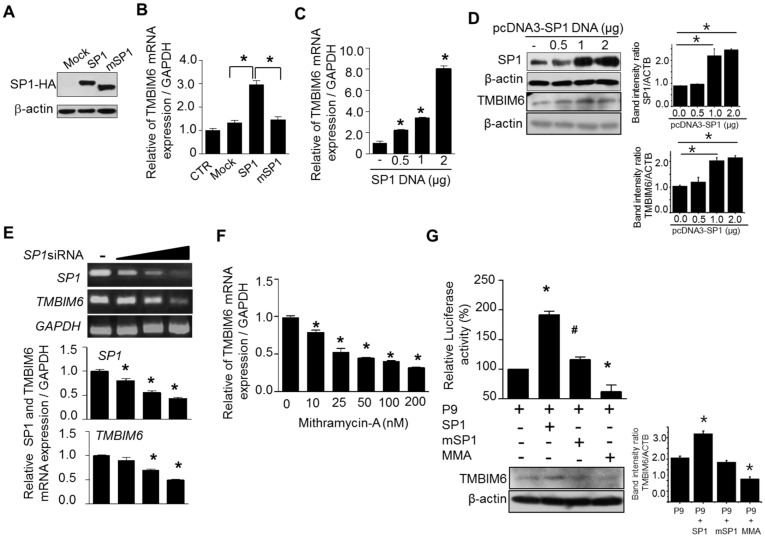
Figure 5.
Sp1 activity and expression level are associated with human TMBIM6 expression pattern. (A) Western blot showing the overexpression of HA tagged Sp1 and deletion mutant of Sp1. (B) The effect of wild type and mutant Sp1 overexpression on TMBIM6 mRNA expression in HT1080 cells, measured by qRT-PCR. The empty vector pCMV-3T3A was used as the vector control (V-CTR); CTR, control non-transfected cells. (C) qRT-PCR analysis of TMBIM6 mRNA levels in HT1080 cells transfected with different concentration of wild type Sp1 construct for 24 h. (D) Western blot showing the Sp1 and TMBIM6 expression levels after transfecting wild type Sp1 in HT1080 cells for 24 h, respective band intensity ratio with β-actin. (E) (upper panel) RT-PCR data showing the Sp1 and TMBIM6 mRNA level after transfection of different concentrations of Sp1-siRNA for 24 h; (lower panel) the respective data of qRT-PCR analysis of Sp1 and TMBIM6 mRNA levels in HT1080 cells. (F) qRT-PCR analysis of TMBIM6 mRNA levels in HT1080 cells after treatment with different concentrations of the Sp1 transcriptional activity inhibitor mithramycin-A for 24 h. (G) The pGL3-P9 construct of TMBIM6 was transiently transfected into HT1080 cells with either wildtype or mutant Sp1 at the ratio of 2:1 for 24 h, and then the cells were lysed and the luciferase activity was measured. The mithramycin-A effect on Sp1-induced luciferase activity with Sp1 overexpression was also tested at the concentration of 200 nM. The pGL3-basic vector was used as the control. The upper panel shows the promoter activity, while the lower panel shows the western blot for TMBIM6 expression and respective band intensity ratio with β-actin under same conditions. The results are the mean ± SD from n = 3 independent experiments. ‘*’ indicate significant differences from the control. ‘#’ indicates the significant difference of P9 activity between Sp1 and mSp1 transfected cells.