Figure 2.
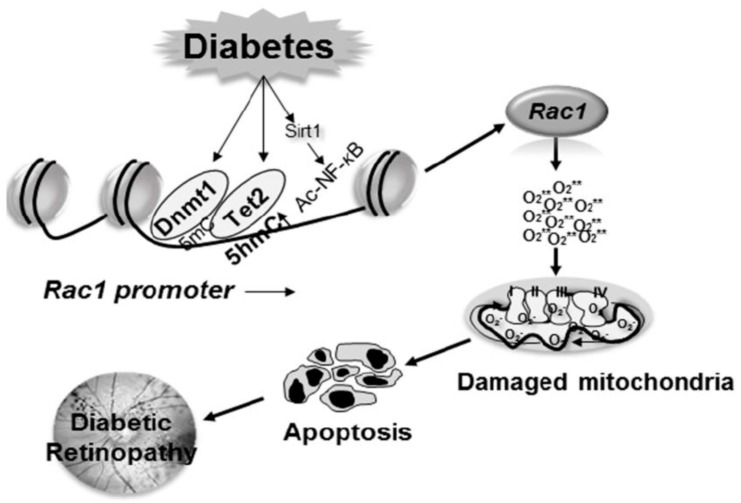
Epigenetic modifications of Rac1 promoter increase its gene transcription. Activation of Dnmts in diabetes increases methylation of Rac1 promoter, but concomitant increased binding of the hydroxymethylating enzyme Tet2, 5mC is hydroxymethylated, opening up the chromatin for the binding of the transcription factors. In addition, due to upregulation of SUV39H1, increase in H3K9me3 levels at the promoter further helps the recruitment of Dnmts and the methylation-hydroxymethylation process. Diabetes also inhibits Sirt1, which allows NF-kB to be acetylated, and facilitating the binding of the acetylated NF-kB at the Rac1 promoter, further helping in Rac1 transcription.