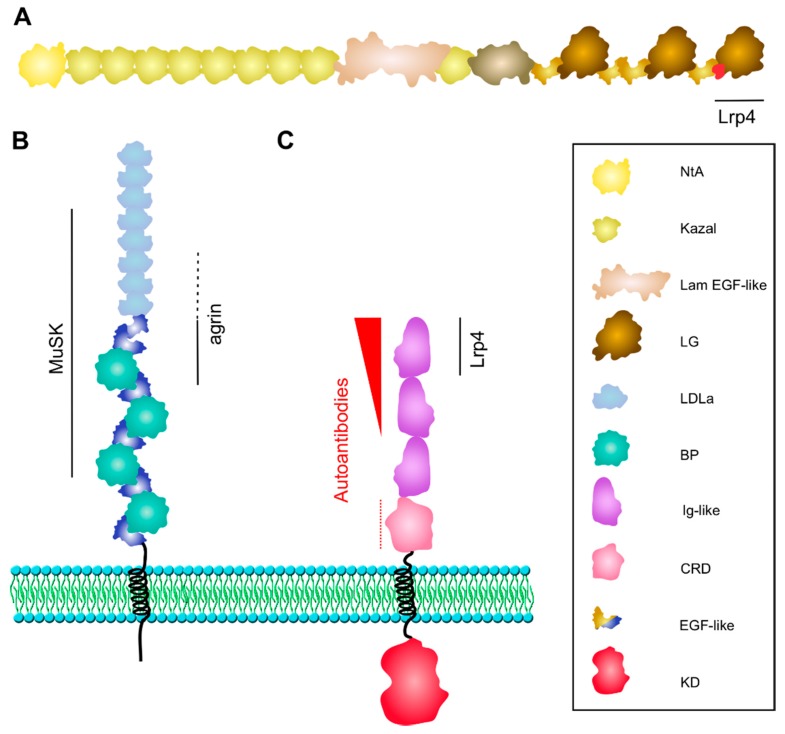
Figure 2.
Structure of Agrin, Lrp4, and MuSK. (A) Neuronal Agrin is anchored in the basal lamina via its laminin-binding NtA-domain. The third LG domain contains the B/Z splice insert (in red), which forms a loop critical for Lrp4 binding. (B) Lrp4 is comprised of a large extracellular domain, one transmembrane domain and a short cytoplasmic tail. The BP domains 1–3 and LDLa repeats 4–8 are sufficient for binding to MuSK. The first BP domain is critical for Agrin binding with supporting function of LDLa repeats 6–8 (dotted line). (C) MuSK interacts with Lrp4 via the Ig1 domain. Ig1 is also important for homodimerization. The kinase domain is phosphorylated and activated upon Agrin-induced binding of Lrp4. MuSK autoantibodies are predominantly directed against the Ig1 domain, less against the Ig2 domain (shown as red arrowhead), and occasionally against the CRD (dotted line). BP, β-propeller; CRD, cysteine-rich domain; LDLa, low-density lipoprotein receptor domain class A; KD, kinase domain; Lam EGF-like, laminin EGF-like; LG, laminin globular-like; NtA, N-terminal Agrin.