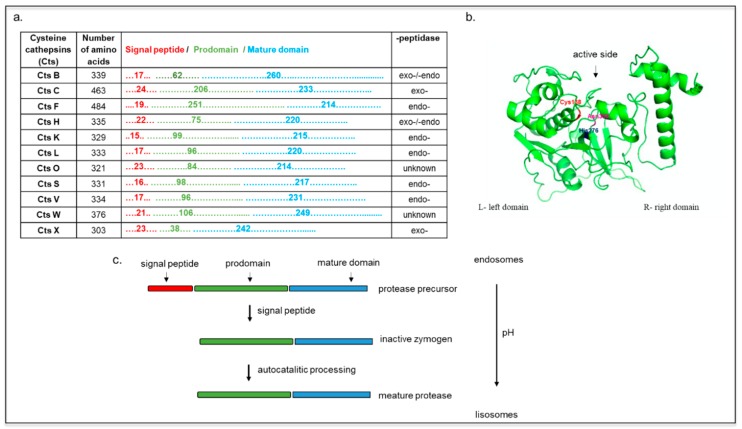
Figure 1.
(a) Cysteine cathepsins (Cts) functional sequences. Representation of Cts according to their number of amino acids, length of domains (signal peptide, prodomain, and mature domain), and peptidase property. (b) Structure of cathepsin L. Cys138–His276–Asn300 triad at the active side is colored (model created with SWISS-MODEL and PyMOL). (c) Scheme Cts maturation as the function of endolysosomal pH. The mannose-6-phosphate pathway favors Cts delivery to endosomes, where they are eventually sorted into the lysosomes. At acidic pH, the pro-peptide is removed, and an active single-chain intermediate is generated. The removal of propeptide is mediated by other proteases (independent of autocatalytic activity). The single-chain molecule is further processed into mature two-chain form comprising an amino-terminal light chain and a carboxyl-terminal heavy chain.