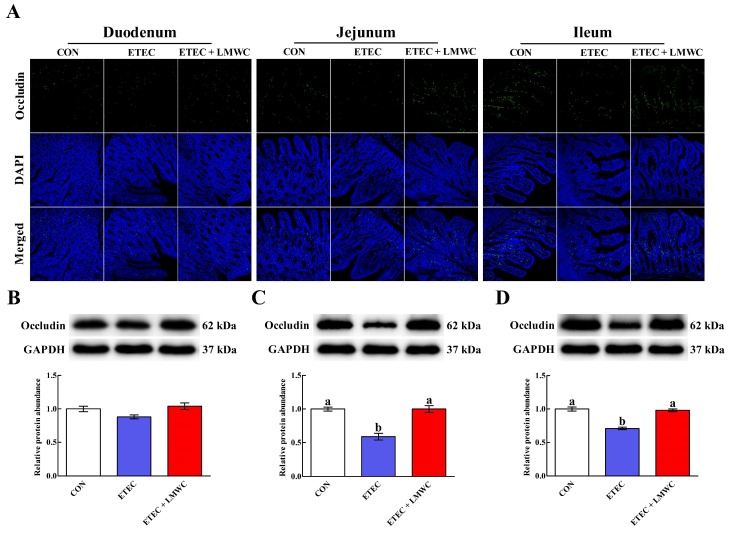
Figure 3.
Effects of low-molecular-weight chitosan on the occludin distribution and expression in the small intestine of weaned pigs challenged with enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli. (A) Duodenal, jejunal and ileal occludin distribution (images were acquired by laser scanning confocal microscopy; magnification ×200). (B–D) Duodenal, jejunal and ileal occludin protein abundance, respectively. a, b Means with different letters on vertical bars indicate significant differences (P < 0.05). Values are means (n = 8 pigs/treatment), with standard errors represented by vertical bars. CON: non-infected control (pigs received the basal diet and infused with sterilised Luria–Bertani culture); ETEC: ETEC-infected control (pigs received the basal diet and infused with enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli); ETEC + LMWC: pigs received the basal diet supplemented with 100 mg/kg low-molecular-weight chitosan and infused with enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli. DAPI, 4′,6-diamidino-2-phenylindole. GAPDH, glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase.