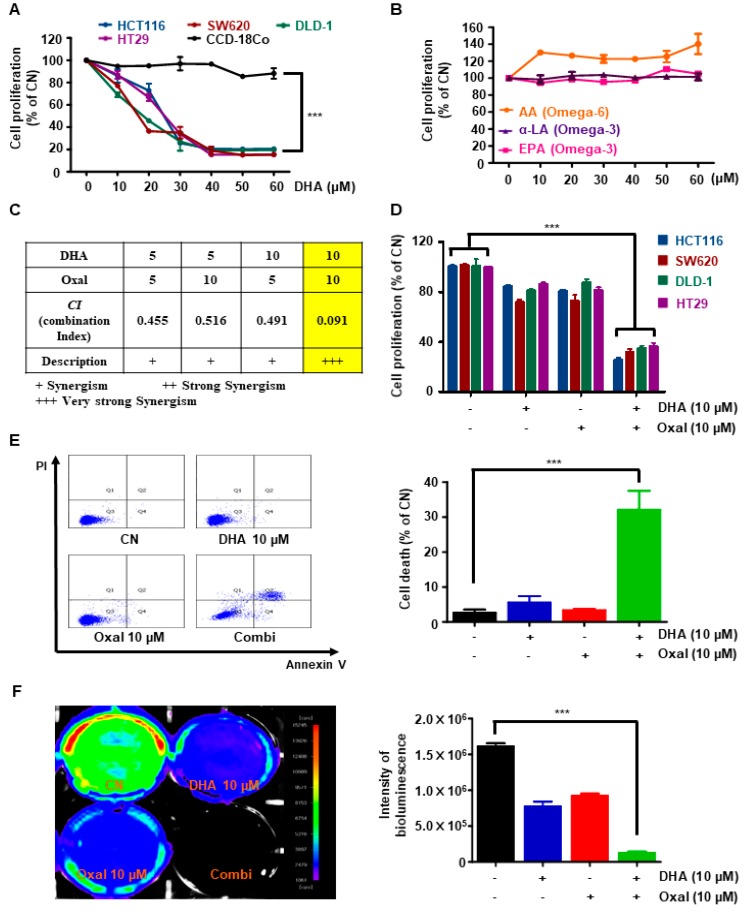
Figure 1.
Combinatorial treatment with Oxaliplatin and docosahexaenoic acid (DHA) reduces viability and induces cell death in human colorectal cancer (CRC) cells. (A) Human normal colon CCD-18Co cells and various human CRC cells were treated with 0–60 µM of DHA for 24 h. Cell viability was measured via a WST-1 assay. ***, p < 0.001; (B) HCT116 cells were treated with 0–60 µM of ω3-polyunsaturated fatty acids (PUFAs) or ω6-PUFAs for 24 h. Cell viability was determined via a WST-1 assay; (C) Combination index (CI) for Oxaliplatin and DHA; (D) CRC cells were treated with the indicated doses of Oxaliplatin and DHA for 24 h. Cell viability was determined via the WST-1 assay. ***, p < 0.001; (E) Cell death was measured via Annexin V/propidium iodide staining using flow cytometry in HCT116 cells. ***, p < 0.001; (F) Intensity of bioluminescence after treatment with Oxaliplatin and DHA in the HCT116 Luc+ cells. The captured images were quantified using Image J. ***, p < 0.001.