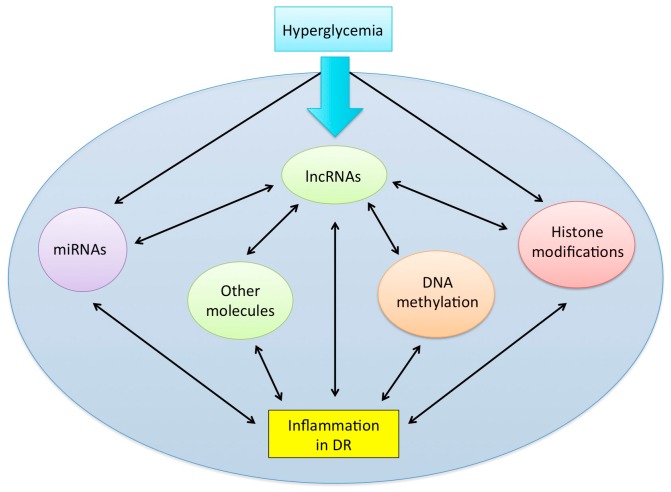
Figure 1.
A schematic depicting the dynamic, coordinated network involving epigenetic modifications in inflammation during DR. Several key epigenetic mechanisms are involved in the progression of inflammation. LncRNAs may serve as critical regulators of inflammation, through their effects on other epigenetic mechanisms, such as DNA methylation, histone modifications, and the activity of other non-coding RNAs (i.e., miRNAs). Furthermore, since the molecular network is heavily coordinated, several individual components of this network may inter-regulate one another, indicated by the double arrows in the figure, and future research should keep these interactions in mind.