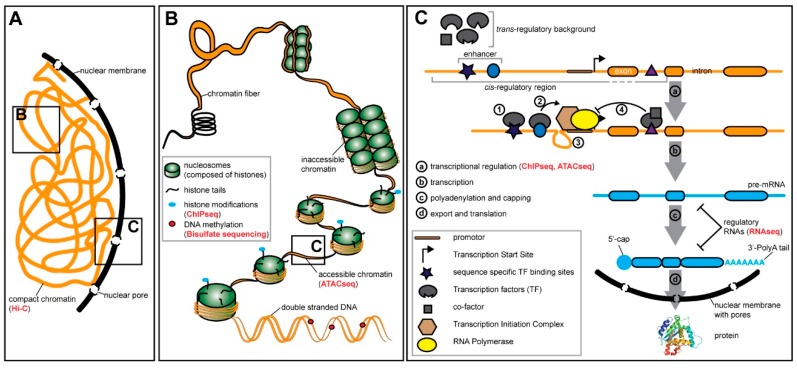
Figure 1.
Gene expression is regulated on various levels. (A) The DNA is compressed in the nucleus of the cell. (B) The DNA in the nucleus is compressed by binding of histone proteins. The chromatin contains easily accessible euchromatin regions and highly compact and inaccessible heterochromatin regions. The status of the chromatin is influenced by post-translational histone modifications. Gene expression is modulated by the chromatin state and DNA modifications, such as methylations. (C) Key steps of gene expression (a–d). Transcription factors (TFs) bind to the DNA at specific sequences (1). TF binding activates the transcription initiation complex (2) through conformation changes (looping) of the DNA (3). TFs can also repress transcription, for instance by binding of a co-factor (4). Next generation sequencing (NGS)-based methods that can be applied to study certain aspects of gene regulation are mentioned in red in brackets. See Table 1 for an overview of the methods mentioned here.