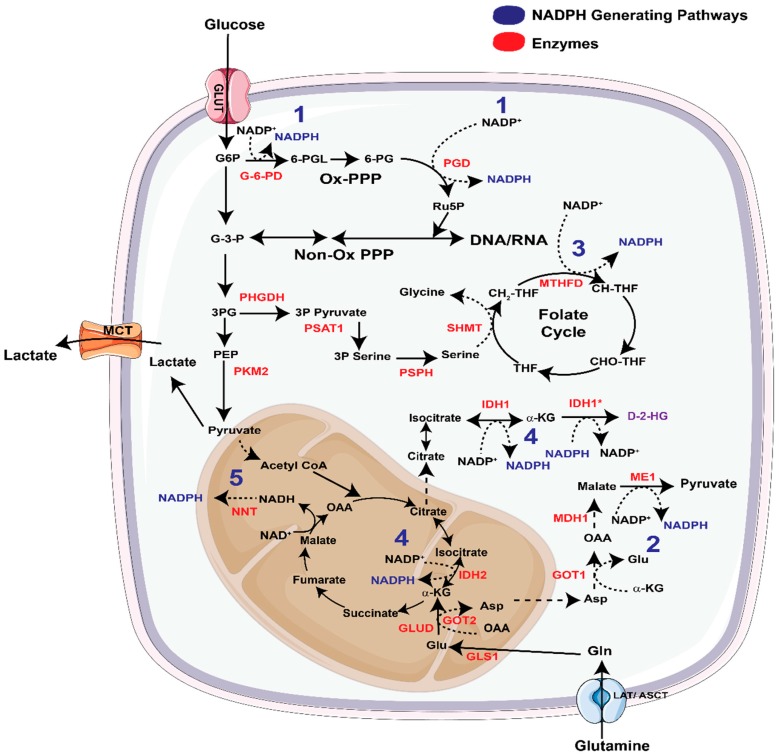
Figure 4.
Altered metabolism as the source of nadph biosynthesis. The principal metabolic pathways that generate NADPH are numbered in blue with key enzymes shown in red. These include (1) the pentose phosphate pathway (PPP) in which conversion of Glucose-6-phosphate (G6P) to 6-phosphogluconolactone (6-PGL) and 6-phosphogluconate (6-PG) to ribulose-phosphate (Ru5P) generates 2 NADPH molecules. (2) Another mechanism of NADPH production is via the conversion of malate to pyruvate by malic enzyme 1. (3) The third reaction mediating NADPH production is the methylenetetrahydrofolate dehydrogenase (MTHFD)-mediated conversion of 5,10-methylenetetrahydrofolate (CH2-THF) to methenyltetrahydrofolate (CH-THF). (ME1). (4) Iso-citrate dehydrogenases (IDH) and (5) nicotinamide nucleotide transhydrogenases (NNT) are other routes of NADPH production in cancer cells. (LAT = Large neutral amino acid transporter, ASCT = Alanine, Serine Cysteine transporter, MCT = monocarboxylate transporters, GLUT = glucose transporter, G-3-P = glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate, 3P serine = 3 phosphoserine, 3P pyruvate = 3 phosphopyruvate, 3PG = 3 phosphoglycerate, PEP = Phosphoenolpyruvate, THF = tetrahydrofolate, CHOTHF = 10-formyl-tetrahydrofolate, OAA = oxaloacetate, Gln = glutamine, Glu = glutamate, α-KG = α-Ketoglutarate, Asp= Aspartic acid, G-6-PD = glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase, PGD = phosphogluconate dehydrogenase, PHGDH = phosphoglycerate dehydrogenase, PSAT1= phosphoserine aminotransferase 1, PSPH = phosphoserine phosphatase, SHMT = serine hydroxymethyltransferase, GLS = glutaminase, GLUD = glutamate dehydrogenase, GOT1/2 = glutamic oxaloacetic transaminase, MDH1 = malate dehydrogenase 1, IDH1* = mutant isocitrate dehydrogenase, D-2-HG = D-2-hydroxyglutarate).