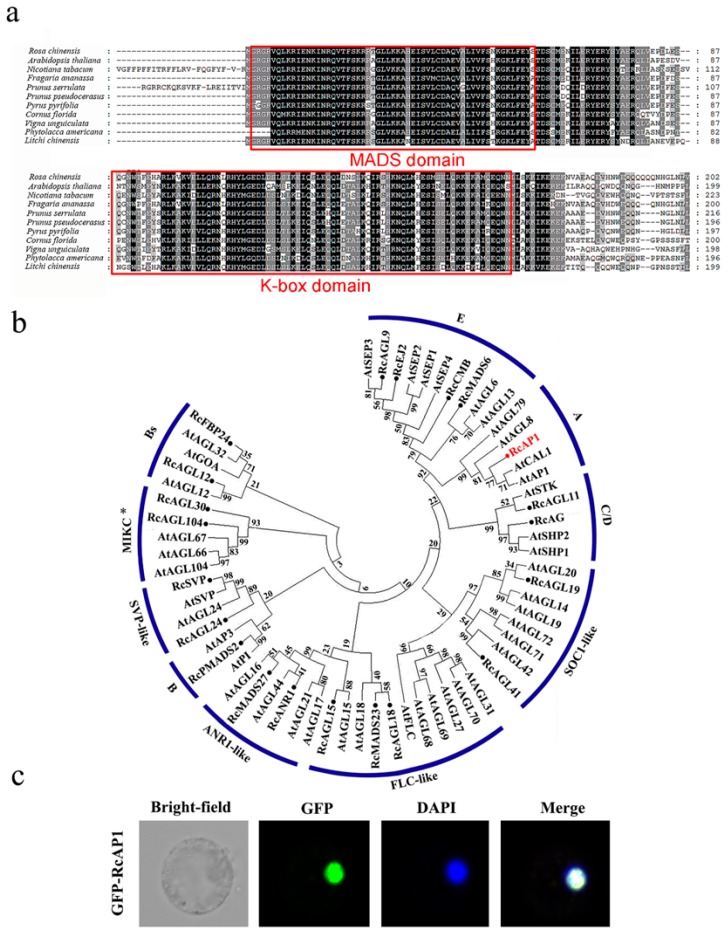
Figure 1.
Bioinformatic analysis of RcAP1 (a) Multiple sequence alignment of deduced amino acid sequences encoded by RcAP1 and other AP1 genes from diverse species. Identical conserved residues are indicated in black, while partially conserved residues are presented in gray. The dotted lines indicate gaps to maximize the alignment. The conserved MADS and K-box domains are framed in red. (b) Phylogenetic analysis of Rosa chinensis and A. thaliana type II MADS-box proteins. A total of 21 R. chinensis type II MADS-box proteins and 41 A. thaliana type II MADS-box proteins were included in a phylogenetic tree constructed according to a neighbor-joining method. The RcAP1 investigated in this study is highlighted in red. The R. chinensis type II MADS-box proteins are marked with solid circles. (c) Subcellular localization of RcAP1. The RcAP1-GFP (Green Fluorescent Protein) fusion protein localized to the nucleus of maize protoplasts.