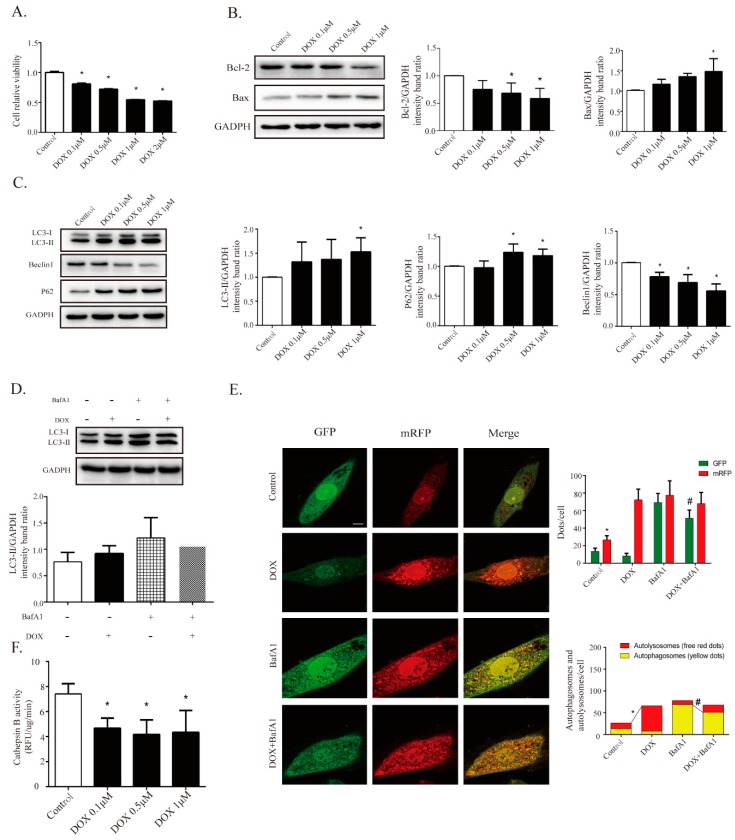
Figure 4.
DOX is found to inhibit cardiomyocyte autophagic flux and lysosomal proteolysis in cardiomyocytes. (A) DOX decreased cell viability in a dose-dependent way via Cell Counting Kit-8 (CCK-8) assay (n = 12). Western blot results showed DOX regulated apoptosis-related proteins, including Bax (n = 5) and Bcl-2 (n = 5), as seen in (B), and autophagy-related proteins, including LC3-II (n = 5), P62 (n = 5), and Beclin1 (n = 5), as seen in (C). (D) BafA1 (100 nM, pre-treated for 4 h) treatment elicited a significant accumulation of LC3-II, and co-treatment with DOX diminished the effect of BafA1 (n = 5). (E) Cardiomyocytes were transfected with GFP-mRFP-LC3 adenovirus to detect autophagic flux with or without BafA1; the DOX-treated cells showed a decline in yellow puncta and an increase in red puncta compared with the control group (n = 30). Scale bar: 50 μm. (F) Measurement of cathepsin B activity in cardiomyocytes (n = 12). All cathepsin B activity measurements are represented as the change in RFU/min corrected to μg of protein. All data are presented as mean ± SD and Student’s t-test. * p < 0.05 is significantly different as indicated, for values in the control group. # p < 0.05 is significantly different as indicated, for values in the BafA1-treated group. BafA1, abbreviation of Bafilomycin A1.